What Is Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning is the process of making sure you have the right resources in place to meet project demands. It helps teams balance workload, avoid burnout, and deliver work on time and within budget.
Summary Overview:
- Coordinate Effectively: Effective capacity planning requires coordination across business, applications, IT, and facilities teams to prevent silos and avoid capacity mismatches.
- Plan Below 100%: Experts emphasize that targeting full utilization is “an economic disaster.” Leave buffer time for learning, variability, and unexpected work. This will improve long-term efficiency and avoid burnout.
- Pay Attention to Digital Infrastructure: Capacity planning involves ensuring that not only people but also digital systems and infrastructure can scale with business demand. Ignoring infrastructure readiness can lead to costly outages or SLA breaches.
- Balance the Long-Term and the Short-Term: Capacity planning focuses on meeting current demand, while resource forecasting focuses on future hiring, future budgeting, and other long-term priorities. Both should ideally be used in tandem for maximum impact.
Why Is Capacity Planning Important?
Capacity planning is important to overall client satisfaction. The process allows a business to match current capacity with future demands, as analyzing capacity data ensures that teams are productive and projects don’t fall behind schedule or run over budget.
Capacity planning is critical to project success because it:
- Prevents Delays Without Overworking Teams: For example, if a product launch requires last-minute support and the team is at full capacity, work might get rushed or delayed. Planning helps shift timelines or reassign work earlier.
- Improves Delivery Predictability: When teams know what’s coming and have the resources to handle it, they’re more likely to deliver on time and avoid last-minute surprises.
- Supports Long-Term Hiring: Capacity insights help you identify when to scale your team. For example, if your team is consistently operating beyond its available capacity, it might be time to hire.
- Helps Meet Stakeholder Expectations: If a service team knows their workload forecast, they can avoid missing SLA commitments and better manage customer demands.
Learn more with this complete guide to resource management.
Richard Gimarc, an independent consultant and author who specializes in capacity management, shares the importance of capacity planning: “If a business is providing a service to its customers, capacity planning ensures the customers are receiving a responsive service and there is a full understanding of the cost of the digital infrastructure required to provide that level of service.”
What Is Capacity Planning in Project Management?
In project management, capacity planning means adjusting team or resource availability to meet project demand. The goal is to deliver efficiently without overloading your team or wasting resources.
Benefits of Capacity Planning
Capacity planning provides transparency into what the team is working on, skill sets, and availability. The number one benefit of capacity planning is that it enables teams to deliver projects on time and within budget.
Below are the top benefits of capacity planning:
- Cost Saving: Capacity planning requires teams to understand resource availability, then helps them identify the most cost-effective way to utilize both human and material resources.
- Skills Inventory: Capacity planning involves making sure every team member has the skills needed for your project and can reveal when they don’t.
- Talent Acquisition: Capacity planning can surface gaps in the organization and the need to acquire talent. Data-informed staffing decisions can swiftly address these gaps.
Gimarc says, “In a perfect world, capacity planners work with their business partners to predict the impact of business demand on the availability and scalability of their digital infrastructure, and then determine the most cost-effective way to optimize service delivery and meet SLAs. Capacity planning is the single source of truth for the business process in question.”
He offers the following example: “How well is the digital infrastructure supporting SLAs and application availability, and what does the future look like based on business demand? Are we near a digital infrastructure breaking point, are we introducing new business services, or are we continuing business as usual?”
Capacity Planning vs. Resource Forecasting: What’s the Difference?
The main difference between capacity planning and resource forecasting is timing — capacity planning is about your current readiness to meet upcoming demands. Forecasting looks ahead to help you prepare for future resource needs.
Resource forecasting is typically done earlier in the process. It supports long-term planning by guiding hiring, budgeting, and project prioritization before work begins.
Check out this guide to resource allocation to get started.
Capacity Planning Strategies
The four main capacity planning strategies are lag, lead, match, and dynamic. Each strategy helps balance resources with demand based on workload, timing, and risk. You can shift strategies as your business needs evolve.
| Strategy | Purpose | Key Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Lag | Use this strategy when you want to keep costs low, adding resources only when demand is clear. | Reactive, conservative |
| Lead | This strategy involves adding capacity in anticipation of high demand. | Proactive, higher risk |
| Match | Use this when you want to grow capacity slowly as demand rises. | Balanced, steady |
| Dynamic | Use this approach when you need to constantly adjust production in advance based on forecasts. | Agile, data-driven |
What Are the Four Key Considerations in Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning depends on alignment across four key areas: business, applications, IT infrastructure, and facilities. Working across these groups can be challenging, but coordination is essential to ensure the right resources are available when needed.
The four key considerations are:
- Business Priorities and Growth Plans: Planning must reflect strategic goals. If leadership expects a new product line to double demand, resource plans must account for additional support across functions.
- Application Requirements and Service Demands: Systems need to be reliable. Capacity planning helps ensure applications have enough support to avoid slowdowns during peak usage or deployments.
- IT Infrastructure Capacity and Scalability: Infrastructure teams must prepare for spikes in usage. Capacity plans guide whether systems can handle increases or need upgrades.
- Facilities Support: In some industries, teams need physical space, equipment, or power. Planning helps avoid scenarios where teams are ready to grow but lack the physical resources to do so.
This collaborative approach is key to reducing resource conflicts and supporting long-term success.
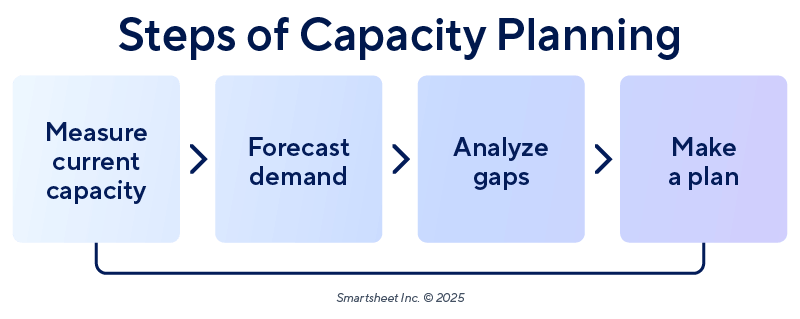
What Are the Steps Involved in Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning minimizes costly mistakes. Teams can begin by measuring current capacity, then they can forecast demand, analyze gaps, and plan for the future.
- Measure Current Capacity: Calculate the total hours your team can work. Subtract time off and meetings.
- Forecast Demand: Use past data or project pipelines to estimate future work.
- Analyze Gaps: Compare demand with available hours. Look for overloads or underuse.
- Make a Plan: Adjust workloads, shift deadlines, or add help as needed
These steps help reduce risk and improve collaboration.
Use these capacity planning templates to measure, forecast, and analyze capacity.
How Do You Manage Capacity Planning?
Capacity planning is not a siloed, one-time activity; it is collective and continuous. Business goals and insight into future growth are crucial to managing capacity. To succeed, you need to continually measure, analyze data, and anticipate the future plan.
“The capacity planning group works for the business. Consider starting out with a line of business that is directly associated with revenue, such as sales,” suggests Gimarc. “The best way to manage capacity planning is to focus on a business owner who is willing to work with you. Once you get the business owner on board, look at metrics and infrastructure that is specific to that line of business.”
Forecasting Resource Needs: Methods, Models, and Tools
When forecasting resource needs, you estimate how many people, hours, or tools you’ll require for a project. You can apply historical analysis, scenario planning, and other methods when forecasting, using PPM software, spreadsheets, and machine learning tools. The right methods and tools can improve accuracy, avoid delays, and ensure efficiency.
Popular forecasting methods and models include:
- Delphi Method: Gather expert input in rounds to reach agreement on future needs.
- Expert Judgment: Use team experience when data is limited.
- Historical Data Analysis: Spot patterns in past projects to estimate future needs.
- Regression Analysis: Connect resource demand to factors such as sales or project size.
- Scenario Planning: Model different project or demand scenarios and see their impact.
- Time Series Modeling: Track resource demand over time to identify trends.
Helpful forecasting tools include:
- Demand Planning Software: This helps you align staffing with projected business demand.
- Machine Learning Tools: Use these to spot complex patterns in large data sets.
- Project Portfolio Management (PPM) or Professional Services Automation (PSA) Software: This is for real-time tracking across projects and teams.
- Spreadsheets: These are used for simple modeling and manual adjustments.
To improve accuracy, integrate forecasting with your resource management system, update it regularly, and use live data when possible.
| Forecasting Method | Tools to Use | How it Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Historical data analysis | Spreadsheets | Spot trends in past projects to predict future resource needs |
| Time series modeling | PPM or PSA software | Track demand over time to plan for upcoming projects with more accuracy |
| Regression analysis | Machine learning tools | Analyze how resource needs relate to external factors such as sales or growth |
| Scenario planning | Spreadsheets, PPM software | Model different workload or staffing scenarios and prepare for potential shifts |
| Expert judgment | Spreadsheets, demand planning software | Combine team experience with flexible tools when hard data is limited |
| Delphi method | Demand planning software | Facilitate group consensus through structured expert input rounds |
How to Do Capacity Planning for Multiple Teams or Departments
To plan capacity across multiple teams or departments, you need shared goals, clear visibility, and consistent prioritization. Align planning efforts so that each team can contribute without burnout or delays.
Follow these best practices:
- Centralize Work Demand: Use one system to collect all incoming project requests across departments.
- Define Shared Goals: Ensure every team understands the broader business objectives.
- Map Team Capacity Separately: Calculate availability for each team to account for differences in skill sets and time.
- Review Plans Together: Hold cross-functional check-ins to resolve conflicts and rebalance workloads as needed.
- Standardize Prioritization Criteria: Apply the same rules for urgency, impact, and feasibility across all teams.
- Use a Unified Planning Tool: Choose a platform to visualize capacity across teams in one place.
This approach helps teams work in sync while keeping projects on track.
Capacity Planning Starter Kit
Download the Capacity Planning Starter Kit
This free capacity planning starter kit includes templates and tools to help you estimate demand, evaluate team capacity, and plan resources effectively. Use it to streamline your planning process, balance workloads, and make smarter project decisions.
Included in this starter kit, you’ll find the following:
- A capacity planning template for Excel to estimate demand, determine capacity, and take appropriate action.
- A team capacity planning template for Excel to get insights into your project team’s resources and anticipate future business capacity requirements.
- A capacity planning checklist in Adobe PDF to guide you through the six main capacity planning considerations.
Project Demand vs. Team Capacity: How to Find the Balance
To balance project demand with team capacity, compare the total workload against your team's real availability. Focus on high-priority work, adjust timelines when needed, and redistribute tasks to avoid overloading certain roles or teams.
Balancing isn’t about doing more — it’s about working smarter. The goal is to match the right people to the right work at the right time. To keep that balance, use shared planning systems and hold regular check-ins. This helps teams spot issues early and adjust before delays or burnout occur.
What Are the Types of Capacity Planning?
A business can use capacity planning to ensure critical resources are available to meet project demands. Here are a few common types of capacity planning:
- Product: A product capacity plan involves ensuring enough products are available to meet deliverables.
- Workforce/Team: An effective workforce capacity plan can ensure that you’ve scheduled an appropriate number of team members and work hours for the project.
- Tool: A tool capacity plan ensures that you have the necessary tools for a project.
- Requirements: Capacity requirements planning (CRP) helps you to establish, measure, and adjust limits or levels of capacity.
- Agile: Agile capacity planning helps teams determine the number of available, productive hours for an upcoming sprint. You will find Agile capacity planning templates in this template roundup.
- IT: Capacity planning for IT involves balancing costs and capacity, followed by supply and demand.
- ITIL: Capacity planning for ITIL services aims to deliver the agreed service level targets under budget and on deadline.
- Rough-Cut Capacity Planning: Rough-cut capacity planning (RCCP) verifies that you have enough capacity to meet the master production schedule requirements.
What Is the Difference Between Capacity Planning and Resource Planning?
Capacity and resource planning are related and complementary. Capacity planning balances the future need for resources against the capacity of resources. Resource planning process functions to allocate people and teams to meet the demands of your projects and programs.
Visit this resource planning guide to learn more.
Capacity Planning Best Practices
Companies can benefit from capacity planning, particularly when available resources continually don’t meet the demands of project work. To adequately plan, you must first gain insight into current capacity and future demand. Below, industry experts share their advice from practical experiences.
Cindy VanEpps, a principle consultant at Project and Team, suggests that capacity planning take place as a team: “Capacity planning is more than just the addition of estimates by each team member. Combining the estimates with building high-performing teams that focus on the same product or outcome helps the team collaborate and identify disruptors.”
VanEpps offers a quote from Donald G. Reinertsen’s book, The Principles of Product Development Flow: Second Generation Lean Product Development: “Operating a product development process near full utilization is an economic disaster.”
Of this statement, VanEpps says, “Reinertsen is correct; planning at 100 percent capacity is an economic disaster. The team must understand the work enough to account for variability imposed by learning. By working in smaller, more manageable batches, the team can allow for potential variability.”
Additional tips for capacity planning include the following:
- Business Alignment: Align work with business goals to maintain your teams' focus on what matters most.
- Team Forecasting: In order for role-based planning to add up to meaningful teamwork, forecast total demand at the team level.
- Understand Current Capacity: Analyze current capacity to plan and know if you can meet current and future requirements more accurately.
- Evaluate Potential Scenarios: Scenario planning can home in on the most valuable combination of investments and types of work that align with your organization's strategic goals.
- Consider Distractions: Remain aware of distractions that sneak into the mix. Consistent monitoring can help your teams stay focused on critical work.
- Anticipate Change: Expect change and anticipate adjustments down the line, often as a result of inaccurate estimates. You may need to reassign resources to stabilize workloads and stay away from bottlenecks regularly.
- Continuous Planning Flow: Continuous planning is necessary because change is inevitable. Capacity planning should also be a proactive process.
- Proactive Planning: Remain proactive in reducing multitasking, minimizing distractions, and streamlining processes to increase productivity.
Mistakes to Avoid When Building a Capacity Plan
Common mistakes in capacity planning include poor forecasting, siloed decision-making, and failing to revisit plans. Teams should avoid these issues in order to stay aligned and meet demand effectively.
Here are some common mistakes when building a capacity plan and how to avoid them:
- Not Having Historical Data: Always ask for historical information, not just current requirements.
- Not Forecasting Demand: Use predictive tools to estimate future workload.
- Planning in Silos: Align cross-functional teams to prevent duplicated efforts, resource conflicts, and blind spots. Encourage shared visibility into priorities and workloads so that departments can coordinate.
- Ignoring Non-Productive Time: Account for everything, not just tasks — this can include time off or other rest time, or time spent on upskilling, research, ideating, and more.
- Ignoring Technology Advances: Stay on top of new tools that improve forecasting, automation, and visibility. Relying on outdated methods makes it harder to anticipate demand.
- Not Understanding Business Objectives: A solid understanding of your organization’s capacity is crucial. Align capacity planning with organizational goals so that teams allocate resources efficiently and focus on the right initiatives.
- Not Understanding the Impact of Change: Anticipate how changes affect workloads and employees. Even minor adjustments can disrupt schedules or stress team members. Evaluate potential impacts before implementing changes.
- Incorrectly Defining Scope: A solid grasp on both timelines and scope will negate the risk of running over time and budget.
- Not Reviewing: Set regular reviews to stay on track, update forecasts, and reallocate resources where needed. Static plans quickly become outdated as priorities shift.
Joao Natalino De Oliveira, Regional Chair and International Officer at Computer Measurement Group, says that the first mistake he sees with startups is the failure to build a capacity plan. “Eighty-five percent of startups fail because they don’t analyze and plan for demand,” he says. “Enterprise companies have dedicated capacity planners. In the early days, these companies preferred to work with large server farms and disk subsystems to sustain during peaks. After several outages, they turned to capacity planning.”
He gives a specific example: “I visited a digital bank with a large number of cloud resources, but without a dedicated capacity planner. They started seeing elevated costs. They saw drastic improvement with a capacity planner that focused on better appropriation.”
Working in silos is another avoidable mistake. As Gimarc says, “Capacity planning should be a point of intersection for the business, application, IT, and facilities teams. Ignoring technology advances is another mistake. Capacity planners should utilize observability information rather than depending on ad hoc documentation and outdated flow diagrams. Finally, a capacity planner must speak the proper language, translating from the business to applications, infrastructure, and facilities.”
Tools for Capacity Planning
Capacity planning tools help teams manage workloads by tracking resources, forecasting demand, and modeling future needs. Common tools include Kanban boards, critical path diagrams, Gantt charts, and capacity planning software. The right tool depends on your project size, complexity, and forecasting needs.
Popular tools for capacity planning include:
- Kanban Boards: Visualize tasks and team workload in real time. Kanban boards make it easy to spot bottlenecks and prevent overload.
- Critical Path Method: Identify key tasks and resource dependencies that affect project timelines. The critical path method is useful for analyzing computing capacity and essential services.
- Gantt Charts: Map tasks over time using a visual bar chart. Gantt charts help coordinate work and track progress against deadlines.
- Capacity Planning Software: Conduct advanced forecasting and scenario modeling, and get real-time visibility into resource availability. A tool such as Resource Management by Smartsheet can help you:
- Balance workloads.
- Improve productivity by centralizing your people.
- Leverage time tracking to improve project estimates.
- Forecast hiring needs for more informed decision-making.
Here are some tips on how to choose the right tool:
- Use Kanban boards for fast-moving or Agile teams that want to manage work visually.
- Use the critical path method for technical projects where timing and dependencies are key.
- Use Gantt charts for schedule-focused work with clear deadlines and dependencies.
- Use capacity planning software when you need forecasting, reporting, and resource visibility in one platform.
Stay on track with this guide to resource scheduling.
What Is the Difference Between Capacity Planning and Resource Planning?
Capacity and resource planning are related and complementary. Capacity planning balances the future need for resources against the capacity of resources. Resource planning process functions to allocate people and teams to meet the demands of your projects and programs.
Visit this resource planning guide to learn more.
Get the Most Out of Capacity Planning With Smartsheet for Project Management
From simple task management and project planning to complex resource and portfolio management, Smartsheet helps you improve collaboration and increase work velocity -- empowering you to get more done.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.