What Is a Project Team?
A project team is a group of individuals collaborating for a specific time period to deliver a specific outcome. Project teams are often cross-functional and ideally offer a diverse set of skills and perspectives. The task of building the team is one of the most important responsibilities in the project planning process.
What Are the 5 Key Roles of a Project Team?
Before building a team, first understand the five key roles of successful project teams. The project manager, subject matter expert, business analyst, technical lead, and stakeholder cover the basic needs of every project. The team makeup might vary, but these five roles are the starting point for most cross-functional teams.
When team members have clearly defined roles, the right skills for the project, and sufficient capacity to contribute, projects are more likely to be completed on time, on budget, and with high-quality outcomes. However, projects teams fail when skill sets are mismatched, responsibilities are unclear, and availability is overlooked.
- Project Manager: The project manager leads the team, manages the schedule and budget, and ensures that the project stays within scope and on track. This role requires allocating resources to projects, facilitating communication between team members, and mitigating risks. The project manager also serves as the point of contact between the project team and all external parties.
- Subject Matter Expert (SME): The SME contributes technical or domain-specific knowledge that ensures project decisions and the quality of deliverables are in line with industry best practices. SMEs often contribute heavily early in the project planning phase and sporadically throughout execution as guidance is needed.
- Business Analyst: The business analyst translates stakeholder goals into project requirements and ensures that the team meets these requirements. They play a critical role in scope definition early on and in change management throughout the project.
- Technical Lead: The technical lead ensures that the project’s systems, tools, and code are implemented effectively and follow architectural or design standards. They often manage developers or engineers as well as project technologies, and troubleshoot complex technical challenges throughout the project.
- Stakeholder: Stakeholders might include executives, clients, or internal sponsors who have a vested interest in the project’s outcome. They provide funding, direction, feedback, and approval for key milestones and deliverables. You can prevent misalignment and scope creep by engaging stakeholders early and often.
| Role | Main responsibility and skills needed |
|---|---|
| Project manager | Oversee the project from initiation to completion Key skills: Leadership, communication, scheduling, risk management, problem-solving |
| Subject matter expert (SME) | Provide deep expertise in a specific area relevant to the project Key skills: Specialized knowledge, critical thinking, attention to detail, mentoring |
| Business analyst | Bridge the gap between business needs and technical implementation Key skills: Gathering requirements, stakeholder engagement, process mapping, analytical thinking |
| Technical lead | Oversee the technical direction and execution of the project Key skills: Technical leadership, quality assurance, system design, software architecture, coding |
| Stakeholder | Providing strategic input and approving major decisions Key skills: Strategic thinking, decision-making, communication, alignment with business goals |
Get started with this guide to project resource allocation, including examples, templates, and expert tips.
5 Steps to Build the Right Team for a Project
Building a strong project team is about strategically aligning roles, skills, and capacity with your project’s needs. There are five essential steps to building a high-performing team: defining project goals, identifying project requirements, assessing capacity, aligning roles, and monitoring changes.
Define Project Goals
Before you start building a team, you need to define the project’s scope and goals. What are the project deliverables? What are your deadlines? What are your budget or other resource constraints?
These details will help you identify the types of work involved in the project and the skills and roles required. Involving stakeholders early helps the team avoid misalignment later on.
Identify Skill Requirements
Map out the specific skills and knowledge areas needed to complete the project tasks and deliverables. You can do this by breaking down the work into tasks or workstreams and considering what skills are needed for each task or workstream. This will lay the groundwork for identifying the right individuals for the work. Remember to consider both the technical and soft skills needed.
With this list of required skills and expertise, you’re ready to use skills-based project resourcing — a modern approach to people resource planning where roles and tasks are assigned to people based on what they can do, and not just on their title or department.
Check out this guide to resource planning in project management, including free tools and expert techniques.
Assess Capacity
Before matching roles and people to skills, assess different team members’ availability. Project team capacity planning shows you how much work each person can take on while accounting for their other projects, their working hours and availability, and any upcoming leave or paid time off.
Overallocation can lead to burnout, missed deadlines, and delays, while underutilization can waste resources and budget. Capacity planning is an important step because it’s not just about whether someone can do the work — it’s also about if they have time to do work.
This overview of capacity planning, including a worksheet and checklist, will help you make informed decisions about your resources.
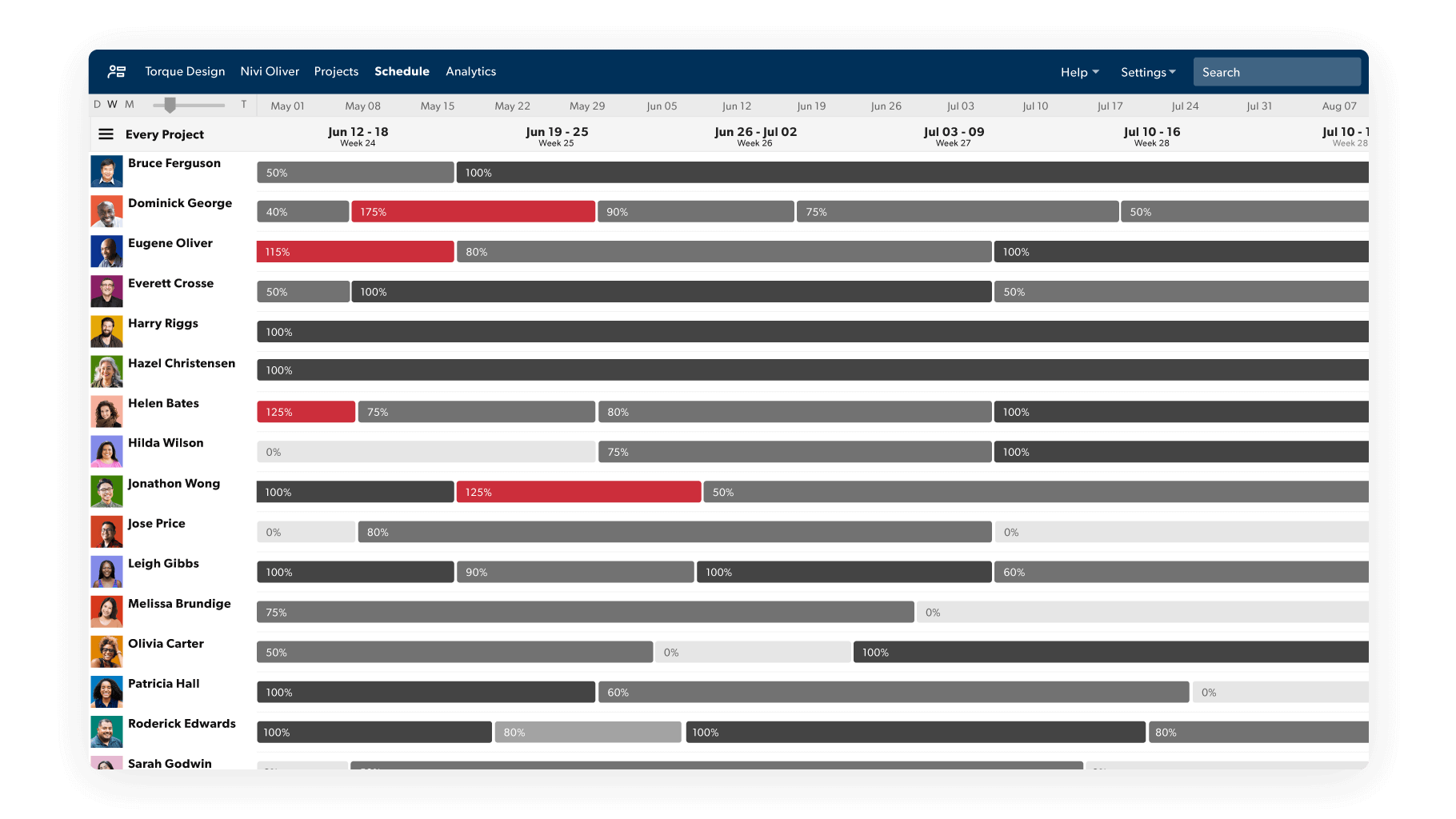
Align Roles and Responsibilities
Once you know the team’s capacity, you’re ready to match people to the skills and expertise needs you identified in step two. Use a RACI or organizational chart to document role assignments and responsibilities. Make sure there are overlaps or gaps to ensure that every task is covered and no task is duplicated.
Monitor and Adjust as the Project Evolves
Changes will inevitably impact your team and project plans. Whether a team member switches roles or the stakeholder sets new priorities, building a team is an ongoing process.
Tools such as Resource Management help teams adapt quickly by syncing with project plans, showing skill gaps and team availability, and supporting reallocation as changes occur. Use a resource management tool to:
Evaluate alignment at each project phase or sprint.
Rebalance workloads and reassign roles based on real-time data.
Communicate changes clearly and early.
Why Team Building and Resource Allocation Are Critical to Successful Project Management
In project management, effective team building and resource allocation are crucial for ensuring that the right team members are assigned to the right tasks and are working on them at the right time. Thoughtful resource allocation makes project teams more productive and minimizes risks.
Resource allocation and capacity planning provide a strong foundation for smart team building — but what’s the difference between these activities? In short, capacity planning defines the limits, while resource allocation ensures that you stay within those limits while maximizing impact.
| Capacity Planning | Resource Allocation |
|---|---|
| Measures how much work a team can take on | Assigns actual work to team members |
| Focuses on availability and hours | Focuses on matching people, skills, and timing |
| Often used for forecasting | Used during project execution and staffing |
Tips for Stronger Project Team Management
Your work isn’t done once you’ve built your project team. Managing a successful project team requires frequent communication, invested team members, continuous adjustments, and the right tools.
Follow these five best practices to strengthen your team at every stage of your project:
Communicate Early and Often: Clear communication from day one builds trust and aligns expectations. Establish communication norms early on — for example, decide on the team’s preferred tools, rules about updates, and response times — to lay the foundation for team success. Share project goals and team roles in the planning process, setting up regular check-ins to monitor progress and blockers. Encourage open dialogue between cross-functional team members.
Involve Team Members in the Planning Process: People are more invested in a plan when they’ve been brought along in the process of developing it. Involve team members during project planning by inviting them to participate in discussions around scope, priorities, and resource needs. Creating a sense of ownership and accountability can also increase individual motivation and uncover hidden skills that might not be reflected in project documentation.
Recognize and Adapt to Team Dynamics: Team dynamics will change as projects evolve. Watch for signs of misalignment or discord within the team, and proactively make adjustments to staffing, workloads, and scope as needed. Regular check-ins and honest feedback loops can help you spot and address these shifts early.
Use a Team Roles Planner: One of the easiest ways to stay organized is by using a tool to map out and document roles, skills, and capacity from the start. Use a Team Roles Planner to identify the key roles your project needs, map skills to tasks, track assignments, and visualize capacity and availability. Revisit your Team Roles Planner as the project progresses and make adjustments as needed.
Leverage Tools That Support Team Building at Scale: Basic tools such as spreadsheets might work for small-scale, simple projects, but for complex projects, purpose-built tools can be more effective in keeping staffing and resourcing decisions clear, flexible, and up-to-date.
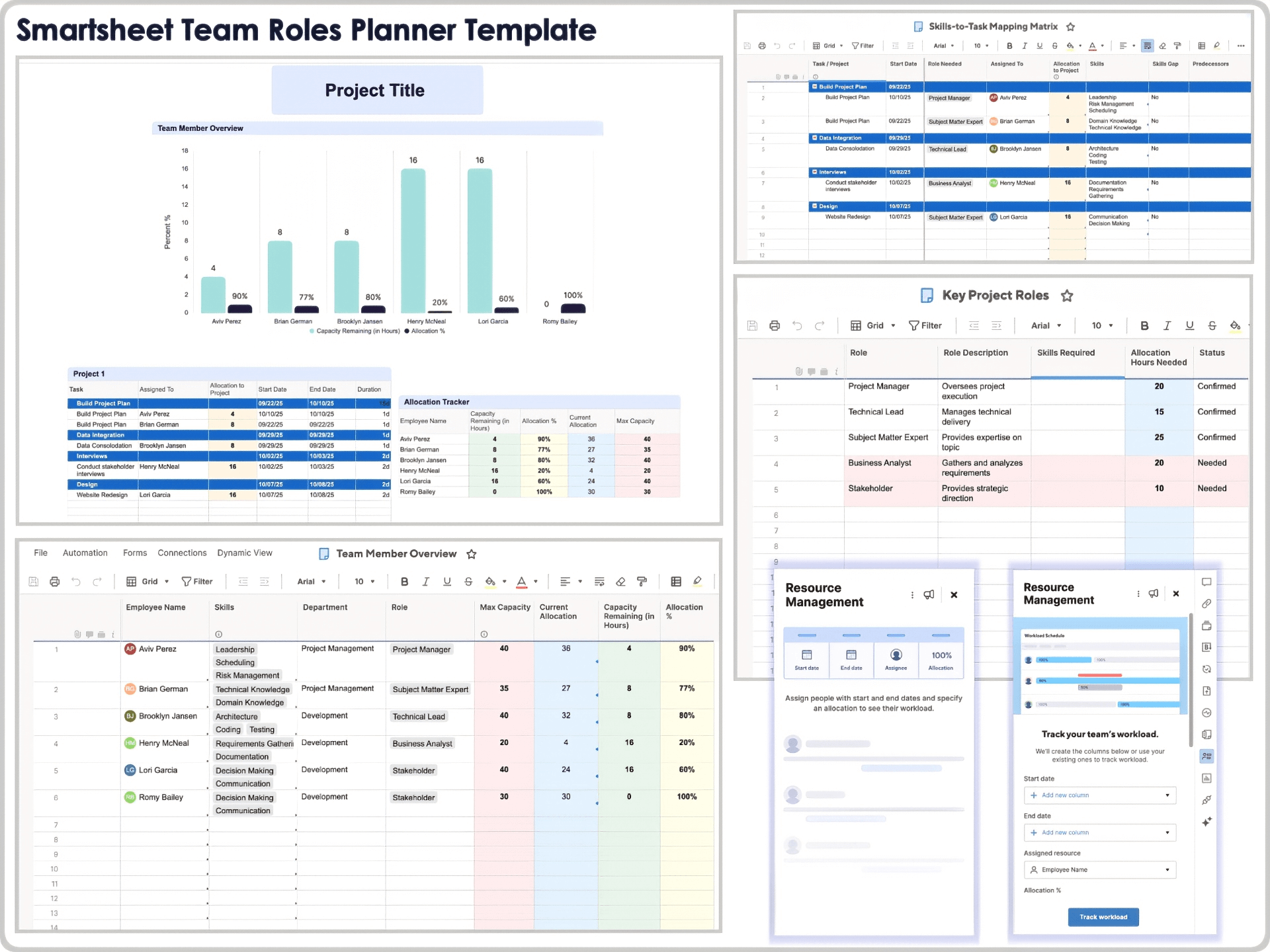
Download the Team Roles Planner Template for
Tools That Streamline Project Staffing
Project staffing tools offer a centralized, real-time view of team capacity and expertise. They simplify scheduling, reduce overallocation, and connect staffing data to project timelines and budgets. This helps project managers adapt to changing priorities.
Many teams still rely on static spreadsheets to track projects, who’s working on what, and who’s available. While this can work for small teams and short-term projects, spreadsheets quickly become outdated and disjointed when larger teams or more complex projects are involved. When your resourcing plan lives in a static document, it’s harder to adjust to shifting timelines and changing priorities, and it requires time-consuming manual updates that often lead to missed deadlines and overallocated team members.
Resource Management is purpose-built to solve these challenges. With a centralized, dynamic view of your people, their skills, and their capacity, you can easily align roles with skills, view real-time availability, forecast capacity, and adjust allocations. Because it integrates with project plans in Smartsheet, your staffing and resourcing data stay connected to your timelines, budgets, and deliverables, helping you make better decisions, faster.
Improve Resource Management Efforts With Smartsheet
Resource Management by Smartsheet is a powerful resource management software that helps to effectively manage the who, the what, and the when behind projects.
With Resource Management by Smartsheet, you can more easily build the best team for a project, keep project schedules and budgets on track, and confidently forecast business needs.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done and by whom, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Watch a free demo to learn more about Resource Management by Smartsheet.