What Is a Project Risk Assessment?
A project risk assessment is a formal effort to identify and analyze risks that a project faces. First, teams identify all possible project risks. Next, they determine the likelihood and potential impact of each risk.
During a project risk assessment, teams analyze both positive and negative risks. Negative risks are events that can derail a project or significantly hurt its chances of success. Negative risks become more dangerous when teams haven’t identified them or created a plan to deal with them.
A project risk assessment also looks at positive risks. Also called opportunities, positive risks are events that stand to benefit the project or organization. Your project team should assess those risks so they can seize on opportunities when they arise.
Your team will want to perform a project risk assessment before the project begins. They should also continually monitor for risks and update the assessment throughout the life of the project.
Some experts use the term project risk analysis to describe a project risk assessment. However, a risk analysis typically refers to the more detailed analysis of a single risk within your broader risk assessment. For expert tips and information, see this comprehensive guide to performing a project risk analysis.
Project risk assessments are an important part of project risk management. Learn more from experts about best practices in this article on project risk management. For even more tips and resources, see this guide to creating a project risk management plan.
How Do You Assess Risk in a Project?
Teams begin project risk assessments by brainstorming possible project risks. Avoid missing important risks by reviewing events from similar past projects. Finally, analyze each risk to understand its time frame, probability, factors, and impact.
Your team should also gather input from stakeholders and others who might have thoughts on possible risks.
In general terms, consider these five important elements when analyzing risks:
- Risk Event: Identify circumstances or events that might have an impact on your project.
- Risk Time Frame: Determine when these events are most likely to happen. This might mean when they happen in the lifecycle of a project or during a sales season or calendar year.
- Probability: Estimate the likelihood of an event happening.
- Impact: Determine the impact on the project and your organization if the event happens.
- Factors: Determine the events that might happen before a risk event or that might trigger the event.
Project Risk Assessment Tools
Project leaders can use various tools and methodologies to help measure risks. One option is a failure mode and effects analysis. Other options include a finite element analysis or a factor analysis and information risk.
These are some common risk assessment tools:
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): This analytical method helps project leaders evaluate a process and identify where the process might fail. The method helps teams identify the failures that could cause the largest impact. By performing this analysis, teams can determine parts of the process that need adjustment.
When using the FMEA framework for risk assessment, identify each of the following components:- Process Steps: Identify all steps in a process.
- Potential Problems: Identify what could go wrong with each step.
- Problem Sources: Identify the causes of the problem.
- Potential Consequences: Identify the consequences of the problem or failure.
- Solutions: Identify ways to prevent the problem from happening.
- Finite Element Analysis (FEA): This is a computerized method for simulating and analyzing the forces on a structure and the ways that a structure could break. The method can account for many, sometimes thousands, of elements. Computer analysis then determines how each of those elements works and how often the elements won’t work. The analysis for each element is then added together to determine all possible failures and the rate of failure for the entire product.
- Factor Analysis of Information Risk (FAIR): This framework helps teams analyze risks to information data or cybersecurity risk.
How to Conduct a Project Risk Assessment
The project manager and team members will want to continually perform risk assessments for a project. Doing good risk assessments involves a number of steps. These steps include identifying all possible risks and assessing the probability of each.
Most importantly, team members must fully explore and assess all possible risks, including risks that at first might not be obvious.
“The best thing that a risk assessment process can do for any project, over time, is to be a way of bringing unrecognized assumptions to light,” says Mike Wills, a certified mentor and coach and an assistant professor at Embry-Riddle Aeronautical University’s College of Business. “We carry so many assumptions without realizing how they constrain our thinking.”
Steps in a Project Risk Assessment
Experts recommend several important steps in an effective project risk assessment. These steps include identifying potential risks, assessing their possible impact, and formulating a plan to prevent or respond to those risks.
Here are 10 important steps in a project risk assessment:
Step 1: Identify Potential Risks
Bring your team together to identify all potential risks to your project. Here are some common ways to help identify risks, with tips from experts:
- Review Documents: Review all documents associated with the project.
- Consider Industry-Specific Risks: Use risk prompt lists for your industry. Risk prompt lists are broad categories of risks, such as environmental or legal, that can occur in a project.
- Revisit Previous Projects: Use checklists from similar projects your organization has done in the past.
- “What I like to do for specific types of projects is put together a checklist, a taxonomy of old risks that you've identified in other projects from lessons learned,” says Wendy Romeu, President and CEO of Alluvionic. “Say you have a software development program. You would pull up your template that includes all the risks that you realized in other projects and go through that list of questions. Then you would ask: ‘Do these risks apply to our project?’ That's kind of a starting point.”
“You do that with your core project team,” Romeu says, “and it gets their juices flowing.”
Learn more about properly assessing lessons learned at the end of a project in this comprehensive guide to project management lessons learned. - Consult Experts: Conduct interviews with experts within and, in some cases, outside your organization.
- Brainstorm: Brainstorm ideas with your team. “The best scenario, which doesn't usually happen, is the whole team comes together and identifies the risks,” says Romeu.
- Stick to Major Risks: Don’t try to identify an unrealistic or unwieldy number of risks. “You want to identify possible risks, but you want to keep the numbers manageable,” says Wills. “The more risks you identify, the longer you spend analyzing them. And the longer you’re in analysis, the fewer decisions you make.”
- Look for Positive Risks: Identify both positive risks and negative ones. It’s easy to forget that risks aren’t all negative. There can be unexpected positive events as well. Some people call these opportunities, but in a risk assessment, experts call them positive risks.
- “A risk is a future event that has a likelihood of occurrence and an impact,” says Alan Zucker, founding principal of Project Management Essentials, who has more than two decades of experience managing projects in Fortune 100 companies. “Risks can both be opportunities — good things — and threats. Most people, when they think about risk assessment, they always think about the negatives. I really try to stress on people to think about the opportunities as well.”
Opportunities, or positive risks, might include your team doing great work on a project and a client wanting the team to do more work. Positive risks might include a project moving forward more quickly than planned or costing less money than planned. You’ll want to know how to respond in those situations, Zucker says.
Learn more about project risk identification and find more tips from experts in this guide to project risk identification.
Step 2: Determine the Probability of Each Risk
After your team has identified possible risks, you will want to determine the probability of each risk happening. Your team can make educated guesses using some of the same methods it used to identify those risks.
Determine the probability of each identified risk with these tactics:
- Brainstorm with your team.
- Interview experts.
- Review similar past projects.
- Review other projects in the same industry.
Step 3: Determine the Impact of Each Risk
Your team will then determine the impact of each risk should it occur. Would the risk stop the project entirely or stop the development of a product? Or would the risk occurring have a relatively minor impact?
Assessing impact is important because if it’s a positive risk, Romeu says, “You want to make sure you’re doing the things to make it happen. Whereas if it's a high risk and a negative situation, you want to do the things to make sure it doesn't happen.”
There are two ways to measure impact: qualitative and quantitative. “Are we going to do just a qualitative risk assessment, where we're talking about the likelihood and the probability or the urgency of that risk?” asks Zucker. “Or are we going to do a quantitative risk assessment, where we're putting a dollar figure or a time figure to those risks?”
Most often, a team will analyze and measure risk based on qualitative impact. The team will analyze risk based on a qualitative description of what could happen, such as a project being delayed or failing. The team may judge that impact as significant but won’t put a dollar figure on it.
A quantitative risk assessment, on the other hand, estimates the impact in numbers, often measured in dollars or profits lost, should a risk happen. “Typically, for most projects, we don’t do a quantitative risk assessment,” Zucker says. “It’s usually when we’re doing engineering projects or big, federal projects. That’s where we're doing the quantitative.”
Step 4: Determine the Risk Score of Each Event
Once your team assesses possible risks, along with the risk probability and impact, it’s time to determine a risk score for each potential event. This score allows your organization to understand the risks that need the most attention.
Often, teams will use a simple risk matrix to determine that risk score. Your team will assign a score based on the probability of each risk event. It will then assign a second score based on the impact that event would have on the organization. Those two figures multiplied will give you each event or risk a risk score.
Zucker says he prefers to assign the numbers 1, 5, and 10 — for low, medium, and high — to both the likelihood of an event happening and its impact. In that scenario, an event with a low likelihood of happening (level of 1) and low impact (level of 1) would have a total risk score of 1 (1 multiplied by 1). An event with a high likelihood of happening (level of 10) and a large impact (level of 10) would have a total risk score of 100.
Zucker says he prefers using those numbers because a scale as small as one to three doesn't convey the importance of high-probability and high-impact risks. “A nine doesn't feel that bad,” he says. “But if it's 100, it's like, ‘Whoa, I really need to worry about that thing.’”
While these risk matrices use numbers, they are not really quantitative. Your teams are making qualitative judgments on events and assigning a rough score. In some cases, however, teams can determine a quantitative risk score.
Your team might determine, based on past projects or other information, that an event has a 10 percent chance of happening. For example, if that event will diminish your manufacturing plant’s production capacity by 50 percent for one month, your team might determine that it will cost your company $400,000. In that case, the risk would have a risk score of $40,000.
At the same time, another event might have a 40 percent chance of happening. Your team might determine the cost to the business would be $10,000. In that case, the risk score is $4,000.
“Just simple counts start to give you a quantifiable way of looking at risk,” says Wills. “A risk that is going to delay 10 percent of your production capacity is a different kind of risk than one that will delay 50 percent of it. Because you have a number, you can gather real operational data for a week or two and see how things support the argument. You can start to compare apples to apples, not apples to fish.”
Wills adds, “Humans, being very optimistic and terrible at predicting the future, will say, ‘Oh, I don't think it'll happen very often.’ Quantitative techniques help to get you away from this gambler fallacy kind of approach. They can make or break your argument to a stakeholder that says, ‘I've looked at this, and I can explain mechanically, count by the numbers like an accountant, what's going on and what might go wrong.’”
Step 5: Understand Your Risk Tolerance
As your team considers risks, it must understand the organization’s risk tolerance. Your team should know what kinds of risks that organizational leaders and stakeholders are willing to take to see a project through.
Understanding that tolerance will also help your team decide how and where to invest time and resources in order to prevent certain negative events.
Step 6: Decide How to Prioritize Risks
Once your team has determined the risk score for each risk, it will see which potential risks need the most attention. These are risks that are high impact and that your organization will want to work hard to prevent.
“You want to attack the ones that are high impact and high likelihood first,” says Romeu.
“Some projects are just so vital to what you do and how you do it that you cannot tolerate the risk of derailment or major failure,” says Wills. “So you're willing to spend money, time, and effort to contain that risk. On other projects, you're taking a flier. You're willing to lose a little money, lose a little effort.”
“You have to decide, based on your project, based on your organization, the markets you're in, is that an ‘oh my gosh, it's gonna keep me up every night’ kind of strategic risk? Or is it one you can deal with?” he says.
Step 7: Develop Risk Response Strategies
Once your team has assessed all possible risks and ranked them by importance, you will want to dive deeper into risk response strategies. That plan should include ways to respond to both positive and negative risks.
These are the main strategies for responding to threats or negative risks:
- Mitigate: These are actions you will take to reduce the likelihood of a risk event happening or that will reduce the impact if it does happen. “For example, if you’re building a datacenter, we might have backup power generators to mitigate the likelihood or the impact of a power loss,” says Zucker. You can learn more, including more tips from experts, about project risk mitigation.
- Avoid: If a certain action, new product, or new service carries an unacceptably high risk, you might want to avoid it entirely.
- Transfer: The most common way that organizations transfer risk is by buying insurance. A common example is fire insurance for a building. Another is cybersecurity insurance that would cover your company in the event of a data breach. An additional option is to transfer certain risks to other companies that can do the work and assume its risks for your company.
“It could be if you didn't want to have the risk of running a datacenter anymore, you transfer that risk to Jeff Bezos (Amazon Web Services) or to Google or whoever,” Zucker says.
These are the main strategies for responding to opportunities or positive risks:
- Share: Your company might partner with another company to work together on achieving an opportunity, and then share in the benefits.
- Exploit: Your company and team work hard to make sure an event happens because it will benefit your company.
- Enhance: Your company works to improve the likelihood of something happening, with the understanding that it might not happen.
These are the main strategies for responding to both threats and opportunities, or negative and positive risks:
- Accept: Your company simply accepts that a risk might happen but continues on because the benefits of the action are significant.
“You're not ignoring the risks, but you're saying, ‘I can't do anything practical about them,’” says Wills. “So they're there. But I'm not going to spend gray matter driving myself crazy thinking about them.” - Escalate: This is when a project manager sees a risk as exceptionally high, impactful, and beyond their purview. The project manager should then escalate information about the risk to company leaders. They can then help decide what needs to happen.
“Some project managers seem almost fearful about communicating risks to organization leaders,” Romeu says. “It drives me nuts. It's about communicating at the right level to the right people. At the executive level, it’s about communicating what risks are happening and what the impact of those risks are. If they happen, everybody knows what the plan is. And people aren't taken by surprise.”
Step 8: Monitor Your Risk Plans
Your team will want to understand how viable your organization’s risk plans are. That means you might want to monitor how they might work or how to test them.
A common example might be all-hands desktop exercises on a disaster plan. For example, how will a hospital respond to a power failure or earthquake? It’s like a fire drill, Zucker says. “Did we have a plan? Do people know what to do when the risk event occurs?”
Step 9: Perform Risk Assessments Continually
Your team will want to continually assess risks to the project. This step should happen throughout your project, from project planning to execution to closeout.
Zucker explains that the biggest mistake teams tend to make with project risk assessment: “People think it's a one-and-done event. They say, ‘I’ve put together my risk register, we’ve filed it into the documents that we needed to file, and I'm not worrying about it.’ I think that is probably the most common issue: that people don't keep it up. They don't think about it.”
Not thinking about how risks change and evolve throughout a project means project leaders won’t be ready for something when it happens. That’s why doing continual risk assessment as a primary part of risk management is vital, says Wills.
“Risk management is a process that should start before you start doing that activity. As you have that second dream about doing that project, start thinking about risk management,” he says. “And when you have completely retired that thing — you've shut down the business, you've pensioned everybody off, you’re clipping your coupons and working on your backstroke — that's when you're done with risk management. It's just a living, breathing, ongoing thing.”
Experts say project managers must learn to develop a sense for always assessing and monitoring risk. “As a PM, you should, in every single meeting you have, listen for risks,” Romeu says. “A technical person might say, ‘Well, this is going to be difficult because of X or Y or Z.’ That's a risk. They don't understand that's a risk, but as a PM, you should be aware of that.”
Step 10: Identify Lessons Learned
After your project is finished, your team should come together to identify the lessons learned during the project. Create a lessons learned document for future use. Include information about project risks in the discussion and the final document.
By keeping track of risks in a lessons learned document, you allow future leaders of similar projects to learn from your successes and failures. As a result, they can better understand the risks that could affect their project.
“Those lessons learned should feed back into the system — back into that original risk checklist,” Romeu says. “So the next software development project knows to look at these risks that you found.”
How to Write a Project Risk Assessment Report
Teams will often track risks in an online document that is accessible to all team members and organization leaders. Sometimes, a project manager will also create a separate project risk assessment report for top leaders or stakeholders.
Here are some tips for creating that report:
- Find an Appropriate Template for Your Organization, Industry, and Project: You can find a number of templates that will help guide you in creating a risk assessment report. Find a project risk assessment report template in our project risk assessment starter kit.
- Consider Your Audience: As you create the report, remember your audience. For example, a report for a technical team will be more detailed than a report for the CEO of your company.
Some more detailed reports for project team members might include a full list of risks, which would be 100 or more. “But don't show executives that list; they will lose their mind,” says Romeu.
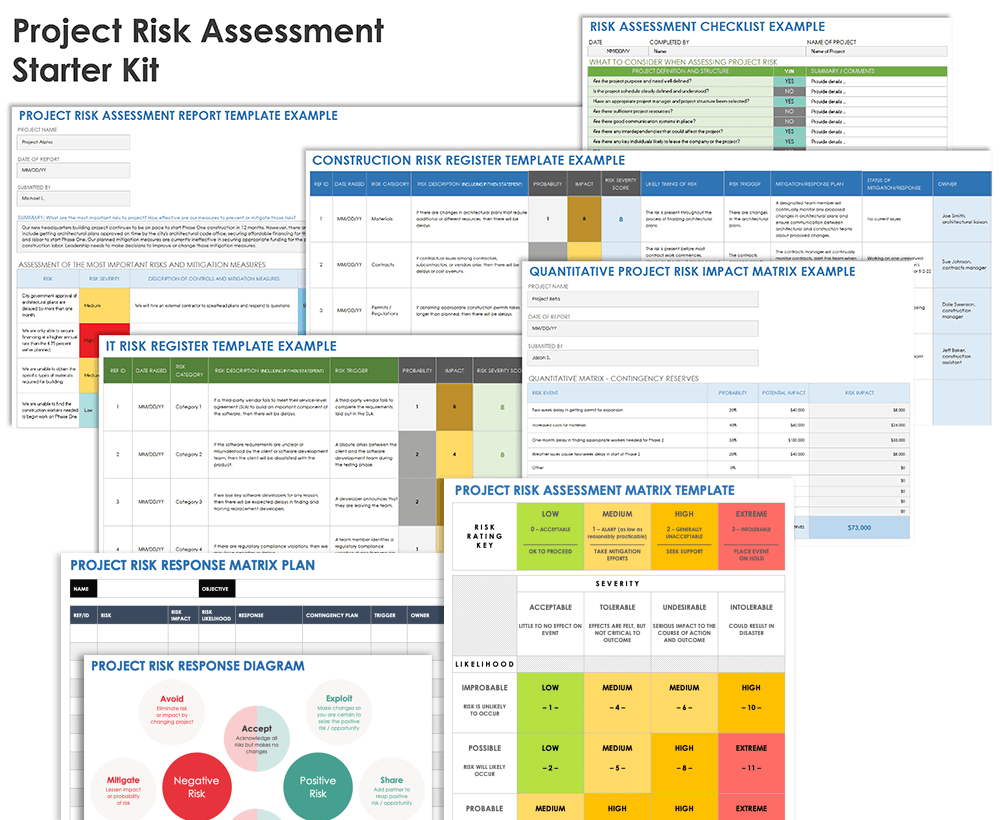
Project Risk Assessment Starter Kit
Download Project Risk Assessment Starter Kit
This starter kit includes a checklist on assessing possible project risks, a risk register template, a template for a risk impact matrix, a quantitative risk impact matrix, a project risk assessment report template, and a project risk response table. The kit will help your team better understand how to assess and continually monitor risks to a project.
In this kit, you’ll find:
- A risk assessment checklist PDF document and Microsoft Word to help you identify potential risks for your project. The checklist included in the starter kit is based on a document from Alluvionic Project Management Services.
- A project risk register template for Microsoft Excel to help you identify, analyze, and track project risks.
- A project risk impact assessment matrix for Microsoft Excel to assess the probability and impact of various risks.
- A quantitative project risk impact matrix for Microsoft Excel to quantify the probability and impact of various risks.
- A project risk assessment report template for Microsoft Excel to help you communicate your risk assessment findings and risk mitigation plans to company leadership.
- A project risk response diagram PDF document and Microsoft Word to better understand how to respond to various positive and negative risks.
Expertly Assess and Manage Project Risks with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.