What Is the Purpose of the Executive Summary?
An executive summary should be clear and concise (typically one to two pages long) and present the main points in a formal tone. The purpose of an executive summary is to pique the reader’s curiosity by presenting facts from the larger piece of content it is summarizing.
The executive summary can be either a portion of a business document (a business plan, project proposal, or report) or long articles and documents common in research-driven communities and academia. When crafted correctly, the executive summary provides an overview of the information and objectives in the larger document. The executive summary stands alone from the content it summarizes, and should include the essential information, the recommendations, the findings, and the conclusion of the more extensive document.
The Benefits of a Well Written Executive Summary
A well planned, well written executive summary is a valuable tool because it prioritizes the reader’s time and reduces the effort required to learn the critical aspects of the content. The summary can convey the purpose of your business plan, project proposal, product launch presentation, or sales pitch to keep the reader engaged and reading further, or empowered to take action. Even if it is the only thing your audience reads, a strong executive summary creates value for the reader as a first impression. Use the executive summary to make a business case, support a position, or tell a story. The reader should know how the subject of your content impacts them, benefits their work, their company, or their projects after reading the executive summary.
Various industries use executive summaries as a communication tool, including healthcare, education, government, technology, real estate, finance, law, the nonprofit sector, and more. One of the benefits of using an executive summary is that it is not exclusive to one type of communication. Executive summaries show up in a variety of use cases, including the following:
-
Business plans
-
Legal briefs
-
Product launch plans
-
College campus surveys
-
Market research reports
-
Environmental studies
-
Project proposals
-
Hospital planning and evaluation
How to Write an Executive Summary
Crafting a useful executive summary requires more than simply cutting and pasting vital information from the body of your report or proposal. The executive summary may be the only part of the report your target audience reads, so you should spend the time to make it valuable.
It doesn’t have to be an intimidating process, but before you begin writing, you should ask the following critical questions:
-
Who depends on the information? When you write the executive summary, decide who you are targeting and the critical information that audience needs. What do they need to know to make a decision? What would they already know? Do you have a specific customer you want to reach with your message or story? Writing the executive summary with that audience in mind will make it useful because the story you’re telling about your business, project, or proposal will resonate.
-
What is the objective? While it’s true that an executive summary recaps essential information from the body of the content it summarizes, that is its function, not its purpose. Write the summary to your intended audience and include the crucial information that supports your objective for creating the document. What do you need the reader to understand? Is the aim to recommend change based on the results of your research? What needs to happen for the project plan to succeed based on your proposal? Let your objectives determine the content and context of your summary.
-
What are you recommending? Use the executive summary to draw conclusions and make recommendations to the reader. If your report presents the need for change, recommend the actions that the body of your document supports in the summary. State the benefits of your product or service, or the solutions you provide more detail on in the proposal. Ultimately, don’t make the reader work to find out what action they need to take: Make your recommendations clear in the executive summary.
-
How will you make an impression? The “executive” summary earned its name from the need to get the upper management’s attention. Executives did not have the time to read every word of every document. The summary had to make an impression because it might be the only part of the material that would be read. Regardless of its origins, the principle of using the summary to make an impression on the reader is sound, as that impression might encourage the reader to keep reading or take action. Consider how you shape the message, organize the sections of your summary, or present research to stand out in a brief space.
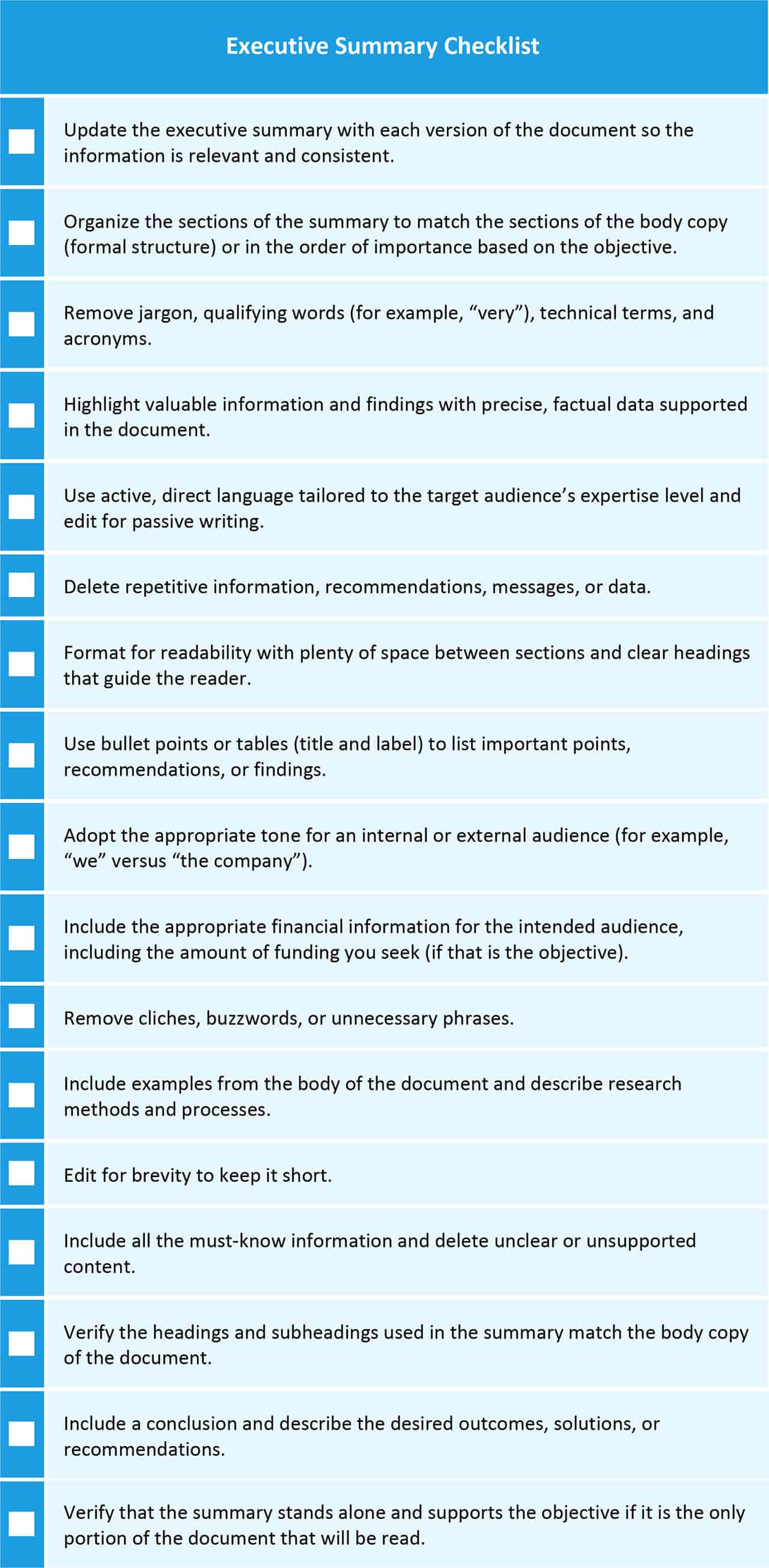
Executive Summary Checklist
After you answer these questions and begin writing your document, refer to the following checklist as you develop the executive summary.
What Is the Format of an Executive Summary?
Every executive summary intends to distill information to the reader upfront, so it is typically placed first in the document. (Sometimes it is a separate section of a formal business document listed in the table of contents.)
When used in a less formal manner, the executive summary is an opening paragraph, a separate one-page summary memo, or the first page of a report. For example, if your goal is to raise capital, use the executive summary like an investor profile that provides the reader the information necessary to land the meeting or get the funding, without further reading.
The format and length vary based on the purpose of the content that you are summarizing; there is no set structure to follow. Here are some formatting tips that you can use for any executive summary, regardless of the style:
-
Order of Appearance: Beyond the introduction, decide what sections of the summary are most important to the purpose of the document. Organize your subheadings or sections in that order. Use bullet points and plenty of spacing between the different parts of the summary to make the content more accessible to scanning eyes. By doing so, you naturally discard information better left to the body of the document, and you honor the reader’s time by prioritizing the message, recommendations, conclusions, or solutions in the longer document.
-
How Much Is Too Much: Executive summaries vary in length based on the type of content they summarize or their purpose. Some recommend keeping the summary to a specific percentage of the overall document, while others advocate a set number of pages. Focus on keeping the summary brief but comprehensive, with the most important information available to the reader.
-
Audience Aim: The tone and language of the executive summary should match that of the target audience. Avoid using technical jargon that requires definitions, and present the information in an accessible manner based on the knowledge and expertise of your intended audience. Do not include acronyms or highlight data that need an extensive background for context, and avoid using casual, informal tones. That said, an executive summary used in internal communications will have a different tone and style than one used in external communication tools.
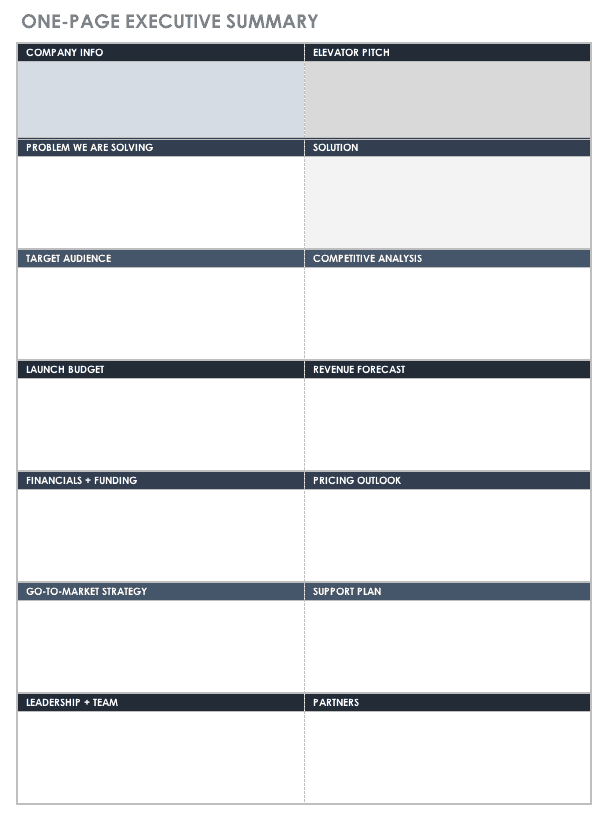
One-page Executive Summary Template
This template is designed to fit your executive summary on one page. Take advantage of the short sections and bullet points to keep the document concise and hook the reader with the information that will keep them reading. Organize the key points by customizing the subheadings to emphasize their importance based on your purpose for the document.
Download One-page Executive Summary Template
What Are the Common Pitfalls of Executive Summaries?
When formatting and organizing the executive summary, beware of the following pitfalls that plague poorly written and poorly planned summaries:
-
Fact or Persuasion: Support your motives and the objective of the executive summary with the facts. If the summary is for a sales proposal or pitch deck, persuade your reader up front with data and information, not buzzwords and cliches. If the executive summary includes generalizations or opinions that you don't support within your material with market research, project examples, independent data, testimonials, etc., you risk misleading the reader. Avoid writing a summary that leads clients, policy makers, or management to an unsupported recommendation or conclusion for the sake of persuasion — instead, focus on the facts.
-
Relevance Over Repetition: By nature, the executive summary is a repetitive summary of content. Therefore, only include the most relevant details — those that summarize the true purpose of the overall content. Use the rest of your business plan, research report, or client proposal to cover topics relevant background information at length. If you try to cut and paste too much information and context from your longer business or research document into the summary, the details might overshadow the impression you want to make on the reader. The background becomes the introduction, and you risk losing a reader’s attention (especially an online audience).
-
Consistency Is Key: The executive summary highlights the substance of the larger piece of content. Don’t feature information here that is not covered in the body of the proposal. Avoid using different subheadings to organize copy in the body of the report. For example, if you highlight “Project Milestones” in the executive summary, do not list them in a new section for “Project Goals” in the business proposal. Use the tone and language you establish in the summary throughout the material. If you target an audience without expertise in the subject matter, don’t switch to highly technical analysis in the body copy. Finally, if you cover something in the executive summary, cover it again in the report. Don’t make the reader work to learn more about something you highlighted in the summary.
-
Draw a Clear Conclusion: Write an executive summary that comes to a conclusion and supports your purpose for creating the document. Keep the reader’s interest in mind when you summarize a lengthy project proposal or report. Does the reader have a clear understanding of the solutions you propose? Can they identify the problems you solve? If the executive summary is the only thing they read, can they take action on your recommendations or anticipate a desired outcome based on the information you included?
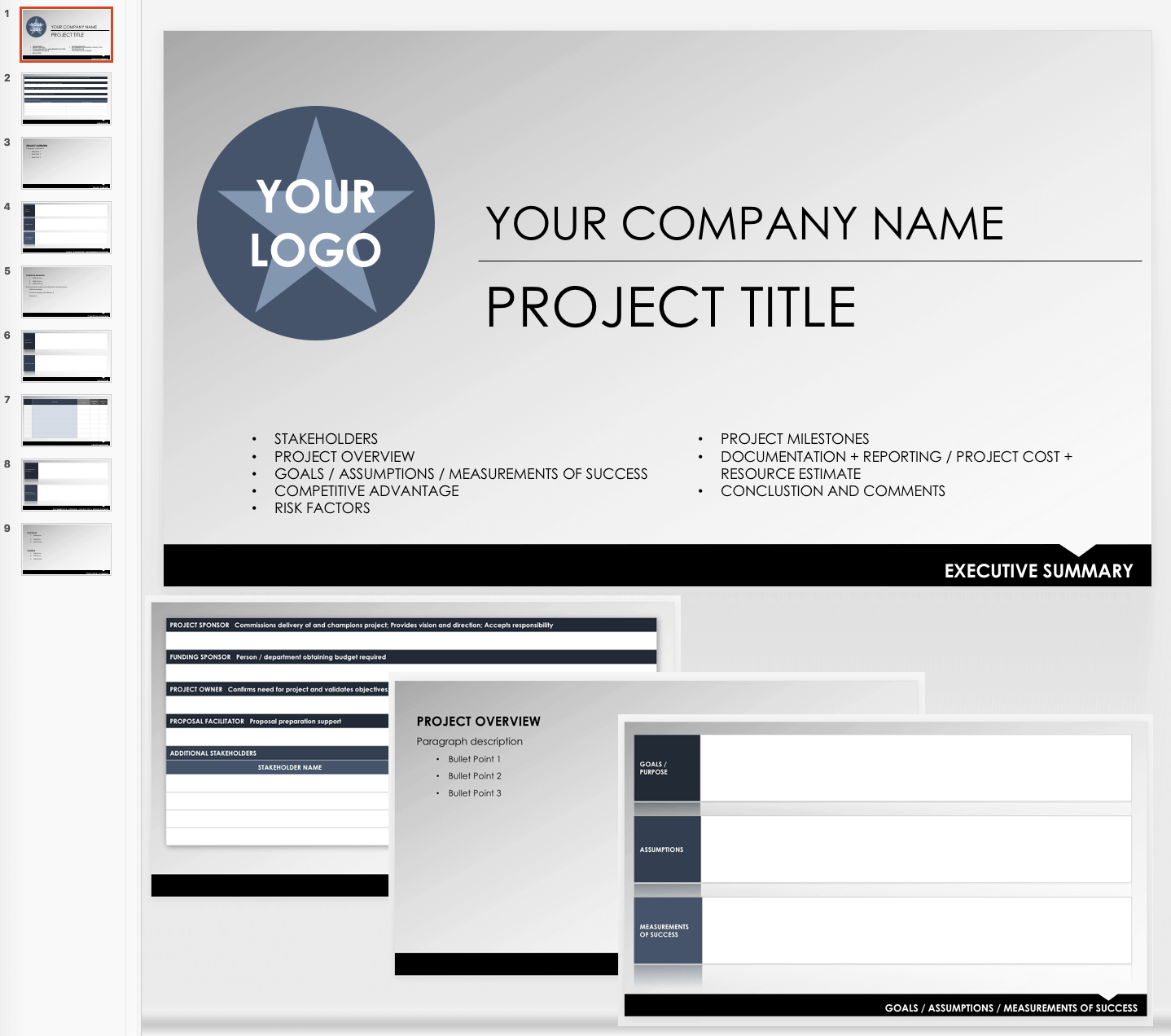
Executive Summary Outline Template - PowerPoint
Use this free template to outline your next big presentation, or keep it updated as a live meeting record to keep up with your evolving internal business plans or funding needs. The slides are formatted to outline the important elements of a formal business plan summary. You can customize the slides to fit the order of importance for your content’s purpose or extend each. Use the slides as an outline to keep track of the content you want to summarize after every update or draft of the report.
Download Executive Summary Outline Template - PowerPoint
What to Include in an Executive Summary
You will determine the components of each executive summary you write based on the reason for writing it and your target audience.
For example, a business plan for an external audience includes financial information and details on the size and scale of a company; startups seeking funding and investors will highlight specific financial requirements and how they impact the business strategy. Executive summaries vary in the content they cover, but here is a common framework:
-
Introduction: This opening statement, paragraph, or section should clearly state the document’s purpose and the content to follow. How you will use this section depends on the desired outcome for the reader or audience, who should immediately find value in the information you present. Therefore, the details included in the introduction should grab and hold the reader’s attention.
-
Company Information: When writing an executive summary for an external audience, include your company name, a description of your mission or purpose, contact information, location, and the size and scale of your operations. In some cases, the summary introduces the founders, investors, and corporate leadership. It might include background information of each that outlines previous industry or startup experience, or historical context on the current state of the company. When used in a presentation or research report, introduce the team presenting or responsible for the report’s findings.
-
Products and Services: The executive summary is the place to highlight the problem you solve or the need you fulfill. For a report, this is where you might highlight what you researched and what the reader should know about your findings. For a project proposal, include what you’re planning to accomplish and what you need to make it successful. For marketing plans or product launch presentations, tell the reader why your service or product is relevant at this particular moment in time.
-
Market Analysis: The executive summary of a business plan might profile the target customer and explain the market opportunity for a product or service. Consider answering questions like: Is there a five year plan for this market? How do you anticipate growing the customer base and improving market share? What stands out from your research about your customers that the reader should know?
-
Competition Analysis: This section should include answers to the following questions:
-
What is the competitive advantage of your proposed solution or product and who or what do you compete with in this market?
-
What are the opportunities now and in the future?
-
What are the risks in your market and your product or service?
-
Do you have relevant experience with major competitors?
-
What are the future plans for growth and what obstacles do you anticipate addressing?
-
-
Financials: The executive summary might summarize key financial data that is relevant to the reader or data that supports your research. If the purpose is to secure funding, include the specific amount you are requesting. Be sure to provide context for the financial data or any number you highlight in the executive summary. This section is a great way to highlight growth, or to use metrics to provide perspective on the company.
-
Conclusions: Recap your findings, the problem and solution discussed, or the project and work proposed. If there is a decision the reader needs to make, be direct about it. Make the outcomes obvious, but leave enough intrigue for the rest of the content to follow.
How Do You End An Executive Summary?
Although the executive summary begins a document, it concludes so that it can stand alone from the rest of the content and still be of value. Use the conclusion to recap your findings, make recommendations, and propose solutions to the problem.
If there is a decision you want the reader to make, ask make a call to action in this section. If you are summarizing a research report, summarize the findings and the research methods used to conclude the work. Make the outcomes or recommendations visible, but leave enough out to incentivize the audience to continue reading. Close the executive summary with a strong statement or transition that sets up the theme or central message to the story you tell in the report or proposal.
What Should Be in the Executive Summary of a Business Plan?
Traditional business plans differ in context and content based on if the audience is internal or external. Both audiences benefit from some of the previously discussed elements of the executive summary (like a substantial introduction).
However, the summary of an internal business plan does not require a section that introduces management or key personnel. An external business plan targets an audience that expects to find crucial financial information in the summary. When you develop the executive summary of the business plan, determine the information to include based on the audience and purpose of the document.
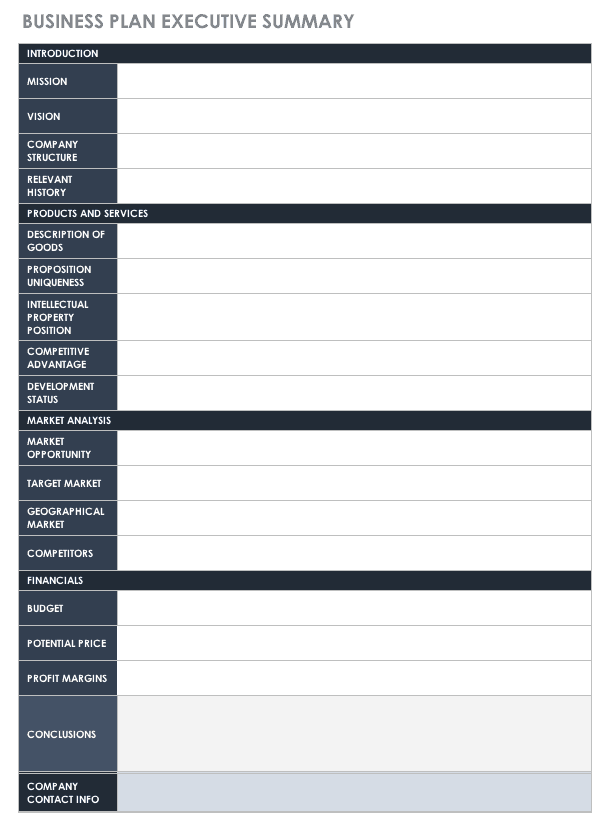
Business Plan Executive Summary Template
This executive summary template is designed to get your business plan noticed and reviewed. In this scenario, you’re presenting to an external audience and therefore should include more attention to detail with a standard business plan document. Use bullet points and clear, formal language to guide the reader to the most important information about your company.
Download Business Plan Executive Summary Template
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
You can find a variety of templates for various industries and needs by reading “Free Executive Summary Templates.”
What Should Be in an Executive Summary of a Report?
Josh Bernoff spent 20 years writing and editing reports for Forrester Research. He is an advocate of creating actionable reports that tell a story. He believes that the executive summary is crucial.
“If the report is a story, the right executive summary is the same story, written briefly,” writes Bernoff. He recommends imagining that your readers ask you questions like, “What’s the coolest stuff in this report?” and “What did you find out?” while writing the report.
“Your answer, written directly to the reader, is the executive summary,” Bernoff explains in his book.
The executive summary of a report requires vivid details that grab online readers’ attention in a hurry. According to Bernoff, the summary recaps the story you want to tell behind all the words in the report. Using this advice as a guidepost, consider including the following answers to these questions to create your report’s summary:
-
What is the central plot of your report?
-
Why is this story important?
-
What are the most memorable scenes (examples, data, case study results, etc.) from the different sections of the report?
-
How does your research address the story’s central conflict (the problem solved)?
-
How does your research support the story’s conclusion?
-
What actions does the story recommend the reader be aware of?
The executive summary of lengthy research reports — especially those used in academic articles, scientific journals, government studies, or healthcare initiatives — require additional formatting considerations and elements not found in business plans or proposals. Consider the following guidelines when developing the executive summary of a research report:
-
Present the sections of the executive summary in the same order as in the main report.
-
Do not include information or research that is not supported and presented in the body of the report.
-
Draw a conclusion with the executive summary that justifies the research and provides recommendations.
-
Use a tone and language to describe technical information that readers without advanced knowledge or expertise of the subject matter can understand.
Remember that an executive summary of a report is distinct from an abstract. Abstracts are shorter overviews of a report and are common in academia. They familiarize the reader with a synopsis of the research that is much shorter than an executive summary. You can also think of an abstract as a standalone statement that helps the reader determine if they will read on. The executive summary, by contrast, summarizes the research in a structure that includes the summary, methods, results, conclusions, and recommendations for the reader without necessarily having to read further.
Research Report Executive Summary Template
Use this template to create a synopsis of research results for reports — these will typically be longer than an executive summary for a business plan and proposal. The template is formatted to accommodate in-depth reports that need space for charts and tables to illustrate research data. It is designed to summarize technical information in a concise manner, with clear subheadings that communicate key findings to readers with various expertise and interest.
Download Research Report Executive Summary Template
Get Funding with Your Executive Summary
Startups seeking capital investment from venture capital funds and angel investors can repurpose the executive summary from a business plan as a more concise, less formal investor profile.
This type of summary memo is stripped down and focused on the specific financial requirements and how the funding makes an impact on the business strategy. It is the perfect template to create a profile on investor platform websites like AngelList and Gust. Use the following tips to transform traditional business plan summaries into the pitch that lands you a meeting or funding:
-
Include the specific dollar amount you’re requesting, the purpose for the funds raised, and any relevant data such as repayment terms, collateral, equity share information, etc.
-
Keep the financial data simple and round to the nearest whole dollar amount.
-
List founders, partners, and key management personnel and highlight specific domain expertise or previous startup experience.
-
Describe your company’s growth plan and the proposed exit strategy.
-
Remove any industry buzzwords, meaningless phrases, and cliches (for example “the Uber of…,” “game-changing,” “disruptive,” “next Facebook,” “world-class,” etc.).
-
Mention noteworthy achievements, intellectual property, important business partnerships, or information on product development stages in test markets.
-
Describe work in progress and highlight relevant information about customer growth, market demand, and product development.
Startup Executive Summary Template
Transform your executive summary into an investor document with this template. It acts as a one-page pitch that serves as your company profile on investor platforms. You can repurpose this template and save it as a PDF summary memo to land future meetings with investors. For more information on business plans for startups, including free budget templates, read “Free Startup Plan, Budget & Cost Templates.”
Download Startup Executive Summary Template
Seamlessly Track the Progress of Your Executive Summary with Real-Time Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.