What Is ISO 22301?
ISO 22301 is a global standard for business continuity planning requirements to help organizations protect themselves against disruptions. The most current version is 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements.
The requirements in ISO 22301 address disruptive incidents that can be natural or human-made, widespread or local, intentional or unintentional, such as a snowstorm, a broken water main, an epidemic, a data breach, or a phishing attack. Large or small, for- and nonprofit organizations alike can use ISO 22301.
The Business Manager’s Quick-Start Guide to ISO 22301
The ISO 22301 standard can provide benefits for your business continuity planning, even if your organization chooses not to pursue certification, or the review process that confirms your business continuity system meets all ISO 22301 requirements.
"Certification is nice, but not required,” says Mart Rovers of InterProm. “First, seek compliance. That way, you know that your business continuity management practices are in better shape." You can start to create a solid business continuity plan with just a few simple steps, which you can also download as this ISO 22301 Quick-Start Guide .
- Check If You Already Have Continuity Plans: Find out if your organization already has business continuity plans. Search through your document management system and ask management or long-time employees. Organizations sometimes create and quickly forget about resources, or store responses locally in an informal system.
As Andrew Nichols of the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center suggests, if your organization already implements other ISO standards, such as ISO 9001 or ISO 27000, you can leverage some of the common requirement elements for your 22301 plan. - Identify Missing Components: Conduct a gap analysis of existing policies and processes to see what business continuity resources you need. According to Mart Rovers, one way to conduct a self-assessment is to copy into a spreadsheet each phrase of the ISO 22301 standard that contains the word "shall." Then, determine gaps between your company and the standard. "Use the standard as your guide to establishing a coherent set of practices to address business continuity management for your organization," says Rovers. You can also use Smartsheet's ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist and ISO 22301 Simplified Cheatsheet for your gap analysis.
- Keep It Simple: Having binders full of perfectly formatted procedures won’t help in an emergency. Create easy-to-follow guidelines and checklists and, more importantly, build "muscle memory" in your employees through training and drills. That way, in a panic, people understand what to do without having to be told.
- Make Your Plan a Living Document: Ticking off items on an audit checklist doesn't mean you’re prepared. Frequently read, revise, and practice your plan to keep it relevant and to train new staff.
- Focus on Recovery Actions: According to Alex Fullick, founder and general manager of business continuity consultancy Stone Road. "Too often, continuity plans are built around a specific scenario.” Don't obsess over whether the disruptive incident is a fire, a flood, or any number of other unforeseeable crises. Instead, focus on what actions can prevent or mitigate damage and what processes and infrastructure you need in order to continue business as usual, no matter the crisis.
- Communicate Your Plan to Staff and Other Stakeholders: Even the most well-written plan is useless if the people who can benefit from it don't know about it. Inform everyone covered by the plan that it exists, including your supply chain and other outside stakeholders.
ISO 22301 Requirements
The ISO 22301 standard offers a framework for planning, testing, and monitoring a business continuity management system (BCMS). The ISO 22301 document contains 10 sections, which introduce the standard and definitions, as well as actionable requirements of the standard.
As with other ISO requirement documents, ISO 22301 describes only what organizations must do to reach minimum proficiency — it does not prescribe how to achieve these standards. Each organization must consider its distinct conditions and obligations to find the best way to follow the requirements.
Here is an overview of the clauses in ISO 22301 that impact an organization most:
- Clause 4, Context: Your organization must understand what it is, what it does, and what outputs and processes it must sustain. You must also determine who has a stake in the continuity of your operations — in other words, the interested parties. For example, customers have a stake in your organization continuing to function.
- Clause 5, Leadership: Few organizational initiatives thrive without the sustained support and championship of top management. Management must commit to a business continuity plan and make available any resources — human, financial, or otherwise — to ensure its success.
- Clause 6, Planning: To plan for sustainability, you must understand what disruptions could potentially occur and how these incidents affect the business — in other words, potential risks and their impact. Set measurable business continuity objectives to guarantee the minimum viable products or services, as well as compliance with any legal or regulatory requirements.
- Clause 7, Support: No program can advance without resources and support. Decide what personnel, roles, and teams you need for threat response and how you can best enhance their effectiveness. Create internal and external communication procedures for reference, and communicate the continuity plan to all necessary parties before and during a crisis. Establish a document management system for key continuity documents, such as procedures.
- Clause 8, Operation: Conduct your risk assessment and business impact analysis, and plan your disruption recovery approach. Implement the recovery plan with detailed procedures, and test it regularly to verify that it works. Make sure people can find the procedures (and other documents) they need, and revise your plan as necessary.
- Clause 9, Evaluation: Establish a process to regularly measure and assess your continuity policies and procedures and their execution. Review and revise your plan and documents to ensure they are effective and relevant
- Clause 10, Improvement: Seek continual improvement in all functional and operational areas, including through periodic management reviews. Improvements in day-to-day activities help bolster the organization in times of disruption. When processes veer from the standard or fail to conform with ISO and quality management standards, implement corrective action.
Key Definitions Related to ISO 22301
Some of the following key terms and concepts originate with ISO, some with ISO 22301, and some with business continuity and risk management:
- Context: The purpose and character of the organization and the environment in which it operates. This includes internal and external influences that shape the business continuity management system.
- Disruptive Incident: A disruptive incident is an event that stops or slows the everyday work of an organization. Examples of disruptive incidents include earthquakes, internet stoppages, broken fans in a data center, or food poisoning in a cafeteria.
- Interested Parties: Interested parties are stakeholders in the successful operation and outcomes of your business continuity plan. They can include customers, employees, suppliers, or regulatory officials.
- Leadership: In ISO 22301, leadership refers to top management or the person or people who run the organization and champion the business continuity effort.
- Maximum Acceptable Outage (MAO): The length of time an activity or process can be unavailable or ineffective before the health and survival of the organization are threatened.
- Minimum Business Continuity Objective (MBCO): The lowest level of products or services that is acceptable for a business to offer during a disruption.
- Recovery Timeframe Objectives (RTO): This refers to the prioritization of key activities and the timing that makes those activities operational.
Benefits of ISO 22301 and Business Continuity Management System
If teams are already overwhelmed with their workload, they may not like to think about disasters. Furthermore, organizations might think that ISO standards include difficult jargon and that pursuing a continuity plan adds unnecessary work. However, management systems practitioners suggest that continuity preparations produce substantial gains.
“I think it's a truism that many organizations can benefit from the principles and some of the practices of resiliency and contingency planning,” says Andrew Nichols, Quality Program Manager at the Michigan Manufacturing Technology Center.
As an example of the benefits that risk analysis and preparation can yield, Nichols relates his experience of visiting a small northeastern town during a widespread winter power outage. The whole town was closed, with the exception of one restaurant that had a generator.
“They had a line of people out the door every mealtime because nowhere else was capable,” Nichols remembers. “Somebody had the foresight to think about the loss of power. And that organization cleaned up financially because they were able to provide what the customers needed.”
Consider these specific benefits to using ISO 22301 business continuity planning:
- Protect against and recover from disruptive incidents.
- Identify and control current and future threats.
- Improve your risk management planning efforts.
- Prevent large-scale damage.
- Become proactive in preventing problems and recovering from incidents, rather than reactive to damage and disruption.
- Reduce downtime and increase recovery time.
- Keep important activities running during disruption.
- Deliver quality products consistently.
- Provide dependable service.
- Prove you’re a reputable supplier.
- Prove your resilience to all stakeholders.
Experts also assert that ISO 22301 can be a simple and effective continuity tool. “All these ISO standards, they’re like hidden gems because of how fast they can get you up to speed without having to reinvent the wheel,” says Mart Rovers, President of IT consulting firm InterProm.
“I cannot emphasize enough how within reach this standard is. Anytime people hear the word ‘ISO,’ they think, ‘Oh, that's for large organizations. Oh, that's way too formal. It's too much. It's overkill.’ I understand where this is coming from because the word ‘standard’ itself is scary for many organizations. However, the size of organization really doesn't matter. The things you should be doing in ISO 22301, you can do at a smaller scale,” says Rovers.
Some also hesitate at the thought of certification. Both Nichols and Rovers stress that certification is not necessary for every enterprise. Although certification may be a condition of doing business for some companies, those who don’t need certification can still gain advantages from following ISO 22301.
In weighing the pros and cons of ISO certification, Rovers suggests buying a copy of ISO 22301, and then copying and pasting each sentence that contains the word “shall” into a spreadsheet (these sentences represent the requirements you must follow). From the spreadsheet, consider whether full ISO adoption and certification are too complicated for your organization. Regardless of your decision, you can always use the spreadsheet to conduct a self-audit.
ISO 22301 in Action
The following image provides a small sample of the possible outcomes to business continuity management.
How a Management System Helps Business Continuity
For those familiar with other ISO standards, the management system component of ISO 22301 might be a new concept. Rovers describes management systems as follows:
“The best way to explain a management system is to imagine opening up an old watch. It has these spinning wheels, these gears. In the case of an ISO standard, you're looking at a number of requirements to put that watch together with all these spinning wheels. That watch is a coherent system. You take out one of those gears, and then the watch fails.
“A management system for continuity follows the same idea — every requirement that the standard asks for represents one of those gears. And every requirement serves a distinct purpose (otherwise, it would not be a requirement). If you don't meet a particular requirement, the watch, so to speak, may not function as it could or should. These ISO requirements are not just there to keep you busy.”
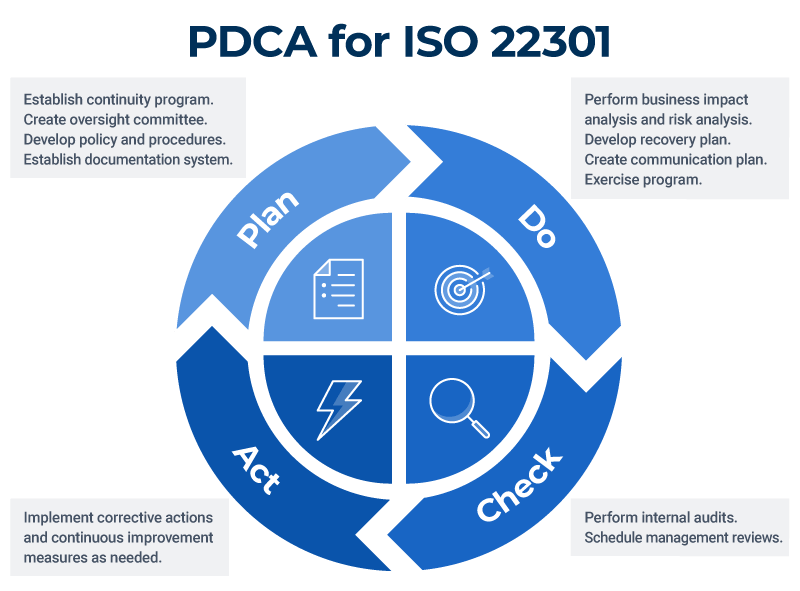
ISO 22301 and PDCA
Each segment of the PDCA (plan-do-check-act) cycle for continuous improvement corresponds to at least one ISO 22301 clause. Organizations can use ISO 22301 to test continuity procedures, review outcomes, and implement updates or fix problems in a continuous cycle that leads to an increasingly resilient business continuity system.
ISO 22301 and Maturity Models
A maturity model measures an organization’s ability to pursue continuous improvement in key areas. ISO 22301 does not have a maturity model.
As Rovers explains, “It was never the intent of ISO 22301 to be a maturity model. You either meet all the requirements of the standard, or you don’t. You could say that by not meeting the requirements of the standard, you’re not mature. Or better said, your business continuity management practices are not mature.”
BCM Lifecycle ISO 22301
The business continuity management (BCM) lifecycle represents industry best practices and some of the core requirements of ISO 22301. These practices offer a solid foundation for resilience, while offering flexibility to adapt to changes in the organization.
Guided by leadership, these are the key activities for the lifecycle:
- Conduct a business impact analysis and risk assessment.
- Establish a business continuity strategy.
- Establish and implement business continuity procedures.
- Exercise and test the procedures regularly before a disruption occurs.
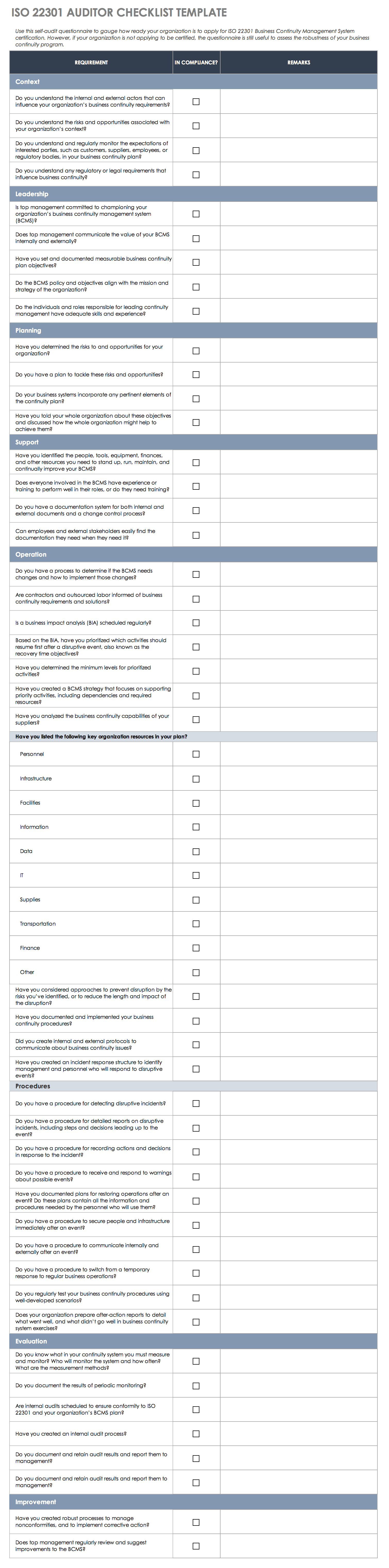
ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template (Excel)
Use this detailed checklist to determine if your business continuity plan aligns with ISO 22301 standards. You can use the template whether you’re applying for certification or simply pursuing a continuity management plan.
Download ISO 22301 Audit Checklist Template
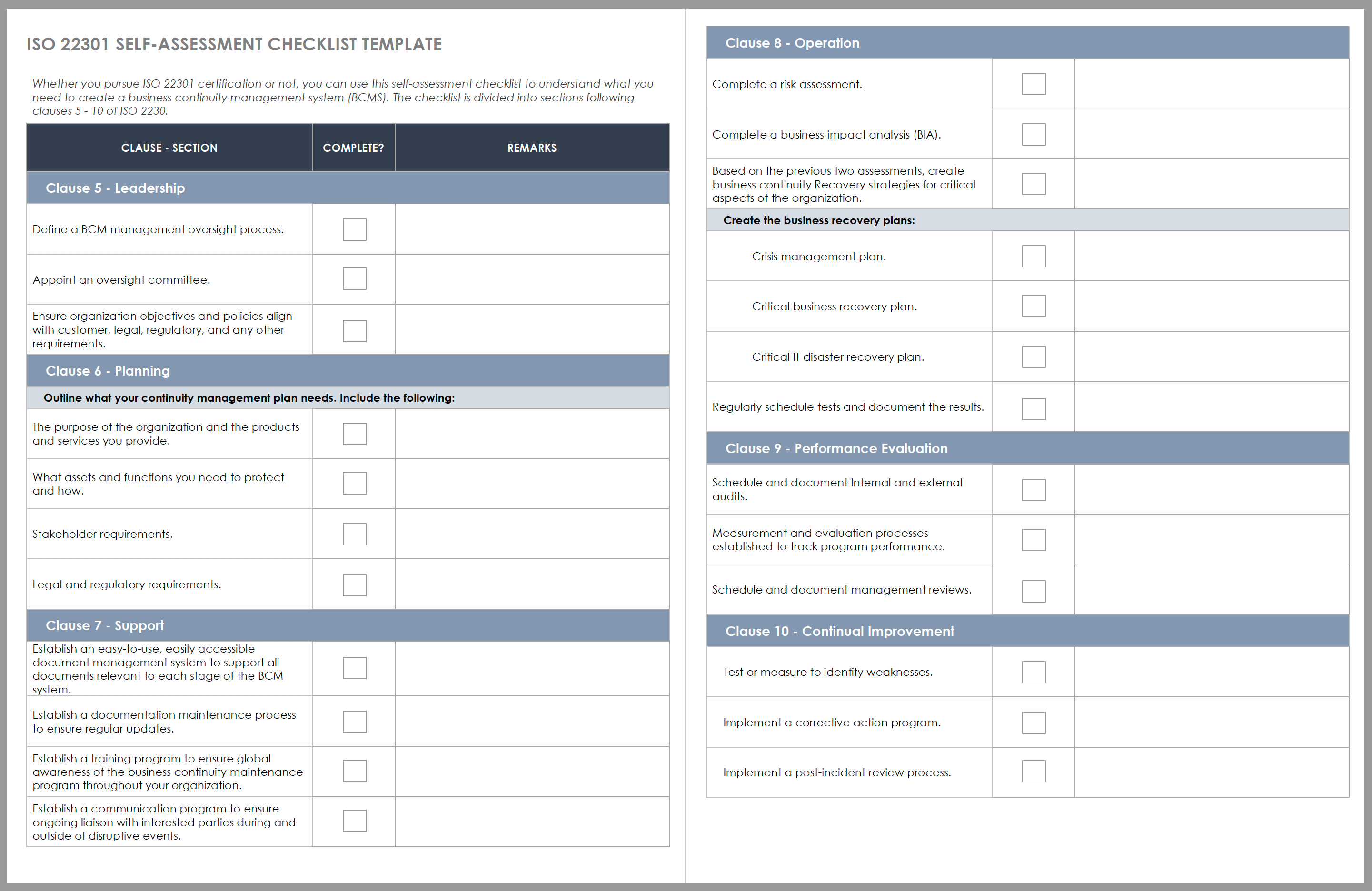
ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist
This self-assessment checklist is divided into sections that correspond to clauses in ISO 22301. Use it to confirm whether your business continuity system meets the requirements for leadership, planning, support, operation, performance evaluation, and continual improvement.
Download ISO 22301 Self-Assessment Checklist Template
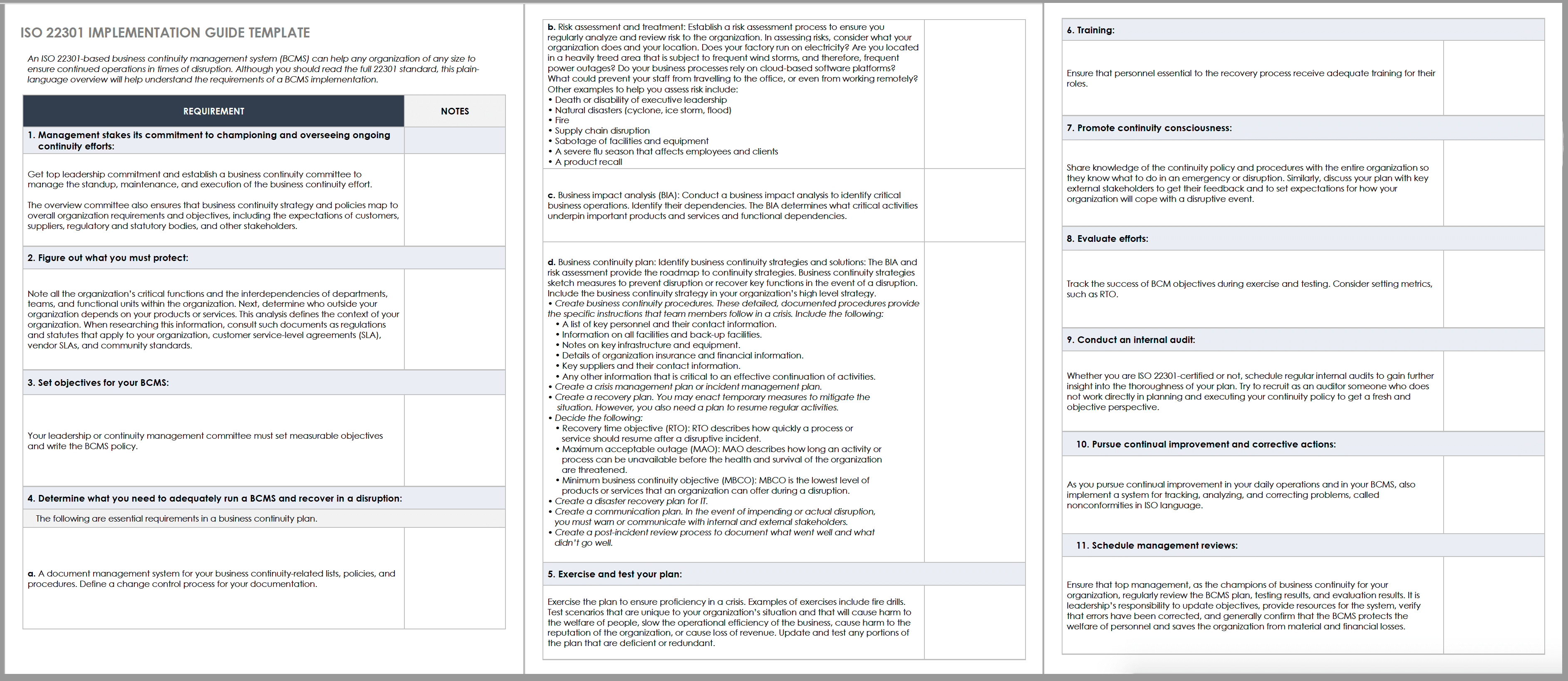
ISO 22301 Implementation Guide
This guide states the essential information from ISO 22301 in plain English. For best results, read it with the full standard, which is currently available for free online to support the COVID-19 response.
Download ISO 22301 Implementation Guide Template
ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet
Use this simplified cheat-sheet to understand the basic elements of creating a business continuity plan. The template walks you through the process of determining critical aspects of your organization, writing the recovery plan, and exercising the plan to ensure proficiency.
Download ISO 22301 Simplified Cheat-Sheet Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
A business continuity policy describes the processes and procedures an organization needs in order to function well daily, including in times of disruption and crisis. This policy template includes space for BCMS objectives, a leadership description, a policy outline, and any certification details.
Download ISO 22301 Business Continuity Policy Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Template
ISO 22301 Business Continuity Sample
The Community Nonprofit Center of New York made available this business continuity template to support the response to coronavirus. Find space to detail responses to minimal and critical emergencies, a risk matrix template, and lists for information about insurance, critical assets, and responses to disruptive events.
For other most useful free, downloadable business continuity plan (BCP) templates please read our "Free Business Continuity Plan Templates" article.
Disaster Recovery Plan Templates
After you perform a risk analysis and business impact analysis, consider writing a disaster recovery plan. Disaster recovery plan templates, available in different formats, provide an easy-to-use structure for documenting continuity plans. Download templates specialized for IT, payroll, small businesses, and more.
To learn about the difference between recovery plans and continuity plans, visit our "Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery: Their Differences and How They Work Together" article.
ISO 22301 Versus ISO 27301
ISO 27301 provides requirements that organizations use to ensure their information and communications technology (ICT) continuity, security, and readiness to survive a disruption. The standard is often staged with ISO 22301 because both are based on similar management system approaches.
The full name of this standard is ISO 27301 - Information Technology - Security Techniques. Originally published in 2011, it is soon to be revised.
“Both [ISO 27301 and ISO 22301] ask for top management involvement and commitment, both ask that you have the right resources, that you have documentation management, that you do performance evaluations, and that you make improvements,” explains Rovers.
They differ in the focus of the risk assessment: ISO 27001 addresses security, whereas ISO 22301 addresses business continuity. “Each area has different risks, but the approach to the risk management assessment and mitigation follows the same steps. There's enormous overlap.”
IT security continuity has significant relevance in the remote work environment. For example, while using your work laptop at home or signed into the work network, what happens when someone innocently plugs in a thumb drive that infects your laptop and corrupts the network? Both ISO 22301 and ISO 27001 work together to prevent such incidents and mitigate problems that occur.
For additional resources, visit "Free ISO 27001 Checklists and Templates."
General Requirements Across Management System Standards
Some ISO requirements are commonly stated across the management system standards, which include ISO 22301; ISO 9001, Quality Management; ISO 20000, IT Service Management; and ISO 27001, Information Security. Examples of common requirements include establishing objectives for the business continuity management system as appropriate to the organization, obtaining management’s commitment to supporting the system, implementing a documentation management system, conducting internal audits, and pursuing continual improvement. This functional overlap enables organizations to undertake combined audits for these standards.
Historical Foundations of ISO 22301
The concept of business continuity was borne out of the IT boom of the 1980s and 1990s. Public and private organizations realized the need to ensure continuity of service and key supplies and to mitigate the effects of disruptive events. The first formal standard reflecting these concerns was the United Kingdom’s British Standard (also known as BS) 25999, which introduced the management system concept to the business continuity discipline.
In 2012, the global standards body ISO released ISO 22301:2012 as the first international standard for business continuity. Based on the contributions and comments of continuity professionals from assorted industries in over 60 countries, ISO 22301 superseded BS 25999.
ISO’s consensus-based standards, such as 22301, cover practices and industries ranging from quality management, IT service, and food safety to environmental safety and information security. ISO standards aim to increase the quality and safety of many products and services, including most common household items, appliances, and cars. Although large enterprises and manufacturers usually follow ISO requirements and guidelines, organizations of all sizes and types can benefit from ISO principles.
For ISO 22301, the standard provides a consistent BCMS framework and a universal language among organizations for communicating about continuity and aligning processes.
When they get certified in ISO 22301 and other ISO standards, organizations can demonstrate to management, legislators, regulators, customers, and other stakeholders that they follow good practices. For ISO certification, organizations need third-party verification that they comply with all requirements of a standard.
“Certification shows you have some level of competence,” explains Rovers. “It shows you take the standard seriously. For organizations buying your goods or services, it can be a compelling reason to choose you.”
Guidance Documents for ISO 22301
For in-depth discussions of aspects of the 22301 standard, ISO offers a series of guidance documents. To those considering pursuing ISO 22301 certification, these documents provide additional insight:
- ISO 22313 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidance on the use of ISO 22301
- ISO 22316 - Security and resilience — Organizational resilience — Principles and attributes
- ISO 22317- Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business impact analysis (BIA)
- ISO 22318 - Societal security — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for supply chain continuity
- ISO 22330 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for people aspects of business continuity
- ISO 22331 - Security and resilience — Business continuity management systems — Guidelines for business continuity strategy
What Is the Latest Version of ISO 22301?
The requirement document ISO 22301:2019, Security and resilience - Business continuity management systems - Requirements, was released on October 31, 2019. The update from the original 2012 version reflects changes in management system approaches and clarifies specifications around clause 8.
Build Powerful, Automated Business Processes and Workflows with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Any articles, templates, or information provided by Smartsheet on the website are for reference only. While we strive to keep the information up to date and correct, we make no representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability with respect to the website or the information, articles, templates, or related graphics contained on the website. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore strictly at your own risk.
These templates are provided as samples only. These templates are in no way meant as legal or compliance advice. Users of these templates must determine what information is necessary and needed to accomplish their objectives.