What Is the Meaning of Human Resource Planning?
Human resource planning, also known as workforce planning, helps organizations recruit, retain, and optimize the deployment of people needed to meet strategic business objectives and to respond to changes in the external environment. In order to proactively avoid talent shortages or surpluses and achieve a balance of talent based on need, effective human resource planning is an ongoing, systematic process.
He says, “Human resource planning and organizational strategy connect at the hip. You can't deliver business strategy without making sure you have the right human capital you need in the right places for the task at hand.”
Smart companies get the human capital part right by implementing a tactical human resource plan that connects directly to organizational and human resource strategies.
Starbucks: Serving Up Human Resources Planning Derived from Mission and Strategy
Starbucks, the world’s largest coffee chain, recorded $21.3 billion in sales for 2016, ranking it at 131 on the 2017 Fortune 500. The company projects that it will reach $35 billion in sales by 2021 by opening 12,000 stores over the next five years, the majority of them in China. How do you plan human resources with such a massive growth goal? For Starbucks, their approach remains the same no matter where stores are located. Their human resource planning flows from its organizational strategy and its brand. People are Starbucks’ primary resource, as their mission clearly states: "Our mission: to inspire and nurture the human spirit – one person, one cup, and one neighborhood at a time."
An important aspect of Starbucks’ human resource planning is its selection process, which uses specific interview techniques to determine if potential employees are ‘on brand’ and evaluate their skill sets. The company identifies capable company leaders and hires them using a program called "New Partner Orientation and Immersion." This human resources planning approach has led to the lowest employee turnover rate among quick-service restaurants. While most quick-serve restaurants range between 150 to 400 percent turnover, Starbucks’ rate is 65 percent. The company is always on the lookout for new employee perks and focuses energy on employee training, which includes an elaborate online portal that offers an instruction program imparting the necessary job knowledge.
The Difference Between Strategic Human Resources Planning and Human Resources Planning
“The war for talent around the world continues to grow.” says Matthew Burr, Moderator of the Upstate HR Podcast and Principal at Burr Consulting, LLC, a human resource consulting firm focused on small and medium organizations. To win the human capital competition, companies should use a strategic human resource plan as a roadmap to achieve three- to five-year goals. Strategic plans influence the development of tactical resource planning (Starbucks being a prime example). For example, a human resources strategic plan may include long-term aims to recruit and retain an excellent staff with a high-level of technical expertise. The tactical plan would include detailed action plans with completion due dates. For the strategic recruitment goals, the tactical program might consist of short-term goals, such as benchmarking salaries via survey data, or creating a social media campaign to identify and recruit technical professionals. The plan may also target filling IT positions through international recruiting.
Both strategic and tactical human resource plans support the overall organizational strategy. To learn more about strategic human resources management, read Welcome to the HR Revolution: Strategic Human Resources Management.
Why Is It Important to Plan Human Resources?
Our world is increasingly one of swift technological change, constant product innovation, economic globalization, and generational and cultural shifts. Correspondingly, the life cycles of business designs and products are shortening. Companies must adapt. More than physical or financial capital, human capital efficiently adapts to this new reality. Simultaneously, human capital is at most significant risk of depreciation or obsolescence within a business — and that’s a risk that organizations can’t afford if they’re going to survive and thrive. In fact, only 12% of firms that were on the Fortune 500 list in 1955 remain on the list in 2016.
- Anticipating Needs in a Changing Workforce Market: According to Deloitte’s 2017 Global Human Capital Trends report, the digital age has created new ways to work. As jobs and skills change, planning and acquiring the right talent is a significant challenge and has caused disruption and risk to more companies.
Murriner says that in the new economy, the importance of having the right people in place has increased, as has their value. “It’s even more apparent, as we move to more knowledge-based work. Historically, our economy has focused on the creation of goods, with an emphasis on materials and equipment. But now more than ever, people costs are the dominant aspect of financial models that support business strategy,” he explains.
- Powering Small and Growth Phase Companies: “Small businesses need to have an HR resource plan to support their overall strategy. They need to plan for when they will hire their next manager, or how many employees their existing management team can support,” explains Laura Handrick, a Senior Professional in Human Resources (SPHR), business coach, former HR Director in Fortune 100 Companies, and writer for FitsSmallBusiness.com.
“Often, small business HR plans will include things like when to stop outsourcing HR, marketing, or finance, and bring a full-time person in-house,” she notes.
The same holds true for franchisors, says Handrick. “They may not have a large staff, but they still need to provide franchisees with HR resource planning tools, not only for the start-up phase but also for growth. For example, a franchisee may start out with only five employees, but once the business gets going, the franchisor can provide them with a plan that shows what the org. structure might look like when they hit 25 employees, 50 employees, and so forth.” - Improving Company Operations: Human capital management and resource planning is a driver for improved company operations and value creation. In July 2017, a group of institutional investors petitioned the Securities and Exchange Commission to disclose policies, practices, and performance of public companies’ human resources management. The petition signifies a move to use workforce analytics to measure the value of an organization’s most valuable asset in a knowledge-based economy.
- Macro Risks Drive a Systematic Approach to Human Resource Planning: “In any company, you have human resource goals related to your business plan. Let’s say, you have 100 people, but will soon need 200. How do we get this to a place where we have exactly the right talent and understand all of those issues that relate to a forward-looking talent basis?” asks Lou Adler, CEO and Founder of The Adler Group, a consulting and training firm. Adler, a top blogger on LinkedIn’s Influencer program, is the author of Hire With Your Head, The Essential Guide for Hiring & Getting Hired, and the Performance-Based Hiring video training program.
Multiple pressures create risk for every hiring organization competing for a less-than-adequate pool of workers with the appropriate skills. Creating a systematic approach to attracting and retaining workers is critical. - The Talent Shortage and Demographic Change: In its 2016/2017 Talent Shortage Survey, the ManpowerGroup reported the highest worldwide talent shortage since 2007. Forty percent of employers are having difficulty filling positions, up from 38 percent in 2015. The Harvard Business Review article, Employers Aren’t Just Whining - the “Skills Gap” Is Real, states that “New technologies frequently require specific new skills that schools don’t teach and that labor markets don’t supply.”
At the same time, there’s a demographic change. In most developed economies, the ‘silver tsunami’ - the group of aging individuals that results from ebbing birth rates and graying baby boomers - is surging. The percentage of the U.S. workforce between the ages of 55 and 64 is growing faster than any other age group. - Technological Change and The New Generation: Millennials now make up more than 50 percent of the current workforce — and will be 75 percent of the global workforce by 2020. Human resources need to ride this rising tide and learn to welcome technological advancements to meet talent’s expectations and business requirements. Talent and workplace analytics will become customary, and organizations using the data will be far more competitive.
- Organizational Change: With technology driving change everywhere, organizations need to be nimble and often make significant changes in the way they do business. They also need to make changes with care. Research shows that change initiatives are more likely to fail because of poor communication, employee resistance, and failure to adequately prepare. Human resources are an integral part of change management, which is a systematic approach that applies tools, knowledge, and resources to deal with business transformation. The primary goal of change management is to successfully implement new processes, products, and business strategies while minimizing adverse outcomes. Effective change management includes and also goes beyond project management and involves leading the "people side" of the change equation.
- Government/Legislative Changes: Each state has regulations that affect everything from employee criminal records checks, labor relations, records retention, and mileage reimbursements. Additional federal laws impact human resource management, too. Consequently, human resource professionals need to be conversant in dynamic employment law to minimize company liability. Not being on top of legislation can pose a significant risk to companies and expose them to expensive lawsuits or damage their brand, which can also be off-putting for potential hires.
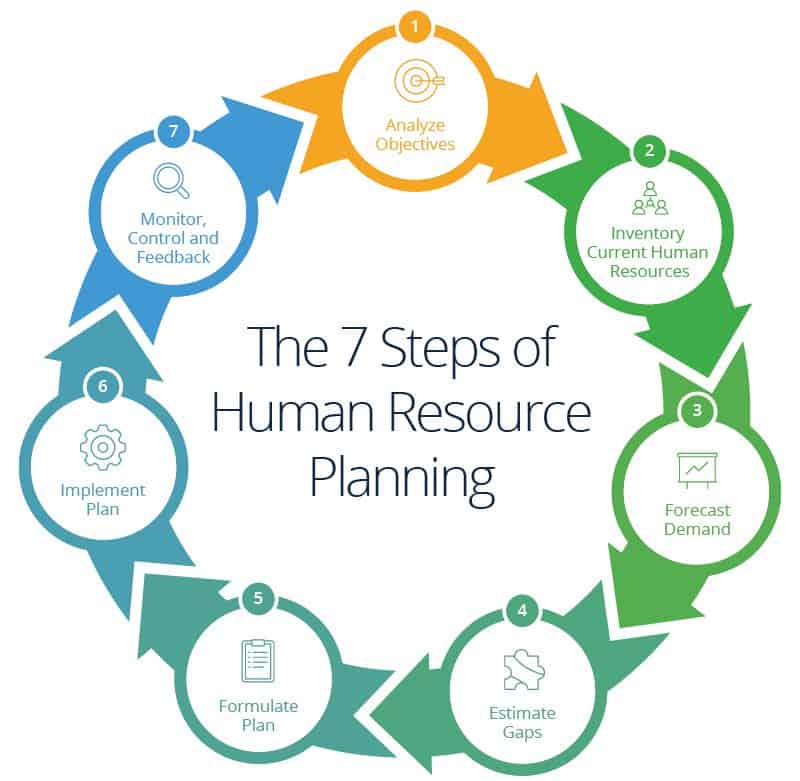
Seven Steps to Human Resource Planning
There are seven different steps in the human resource planning process, but the pivot point is forecasting demand. That means that today’s human resources professionals need to have a well-rounded picture of their own company and a grasp of multiple factors to put together a plan. “Understanding the three- to five-year business strategy provides what HR must have to forecast workforce needs within the firm,” says Burr. “But there’s also a need to understand the global economy and potential growth options, laws, and regulations to add value to any HR strategy and forecast.”
The seven steps to creating a human resource plan provide a roadmap for companies, but one size does not fit all. The amount of detail and which factors to include are different for every organization. Startup sole proprietorships working in a single geographic area will need to create an entirely different plan than a multinational enterprise.
Step One: Analyze Organizational Objectives
Aligning HR practices to strategic objectives is fundamental to an effective human resources plan. In a perfect world, human resources management works hand in hand with other top managers so there is a clear understanding of ultimate goals, and then they focus on the human capital needed to meet them. It’s vital that the human resources plan encompasses every part of the company from product development to sales and expansion plans.
HR Strategic Plan Template
If your company hasn’t written a strategic human resource plan, this template will help you get started. Modify the template to suit your specific needs or to focus on target areas such as benefits or retirement. Stakeholders will appreciate the basic design when they want to review important aspects of your plan.
Download HR Strategic Plan Template
Need more strategic planning templates to clarify goals for your organization? You can find more free strategic planning templates here.
Step Two: Inventory Current Human Resources
If you have one, use the updated human resource information storage (HRIS) system to analyze the number of people you currently employ, along with their skills, performance, and potential. Once you determine which jobs need to be filled based on your forecast, you can then decide whether you have enough internal candidates to fill the job requirements or if you need to go to external sources or strategies to add staff.
Employee Evaluation Template
If you don’t have an HRIS system, you can use this performance evaluation template for performance reviews and as a first step in referencing your current human resource inventory. Adapt this easy-to-use form to gain a better understanding of the duties for each position by identifying gaps in performance and staffing when you review information in the aggregate. This template documents performance against set goals, employee evaluation, and professional development plans for the upcoming year.
Download Employee Evaluation Excel Template
Step Three: Forecast Demand
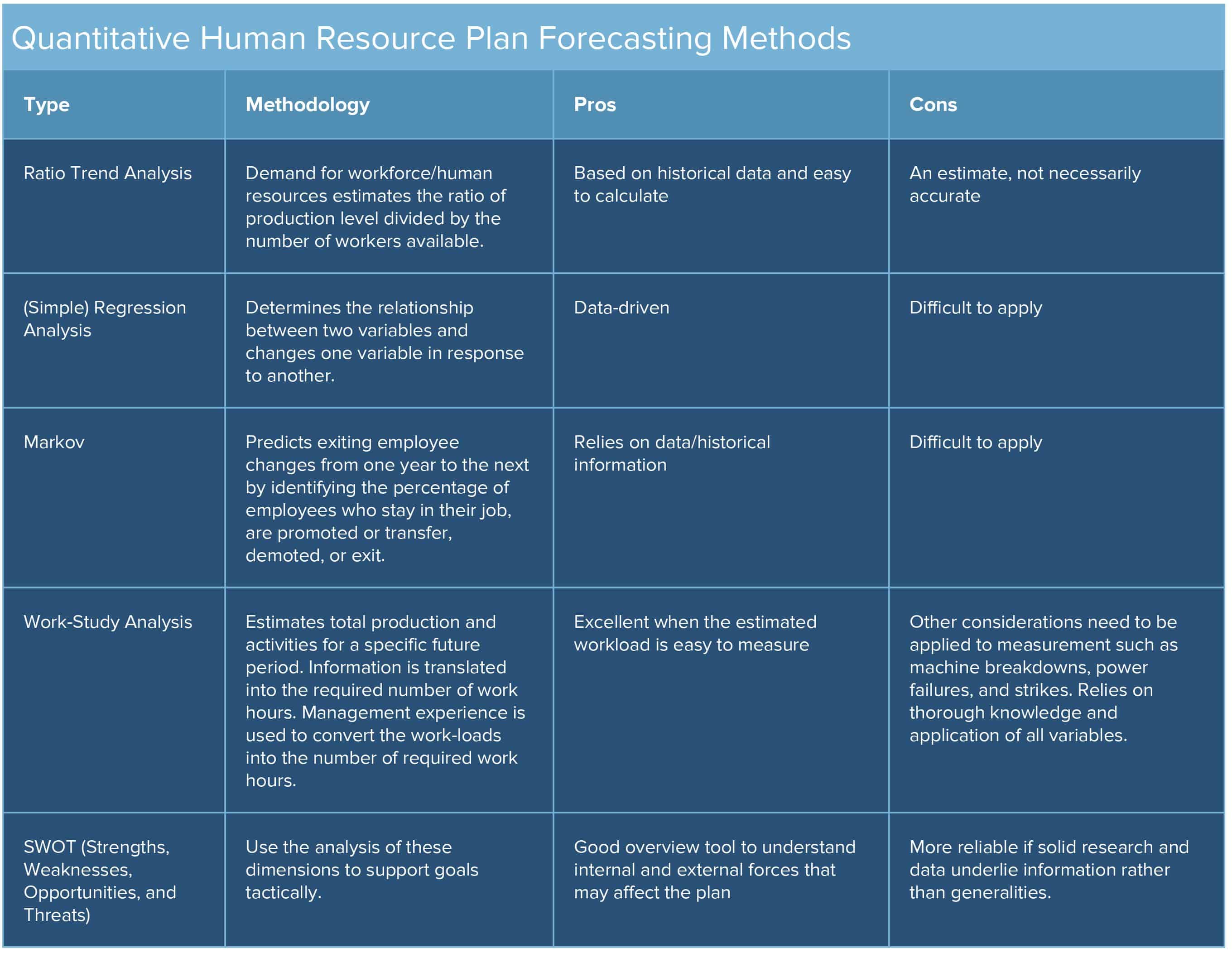
Forecasting human resource demand involves estimating the number of future employees of the right quality and quantity, with a view to the company’s strategic plan over a given period of time. Forecasting demand is the most crucial part of human resource planning and the most daunting. It’s challenging for many reasons, and even more so because there are no absolute answers on how to accomplish it.
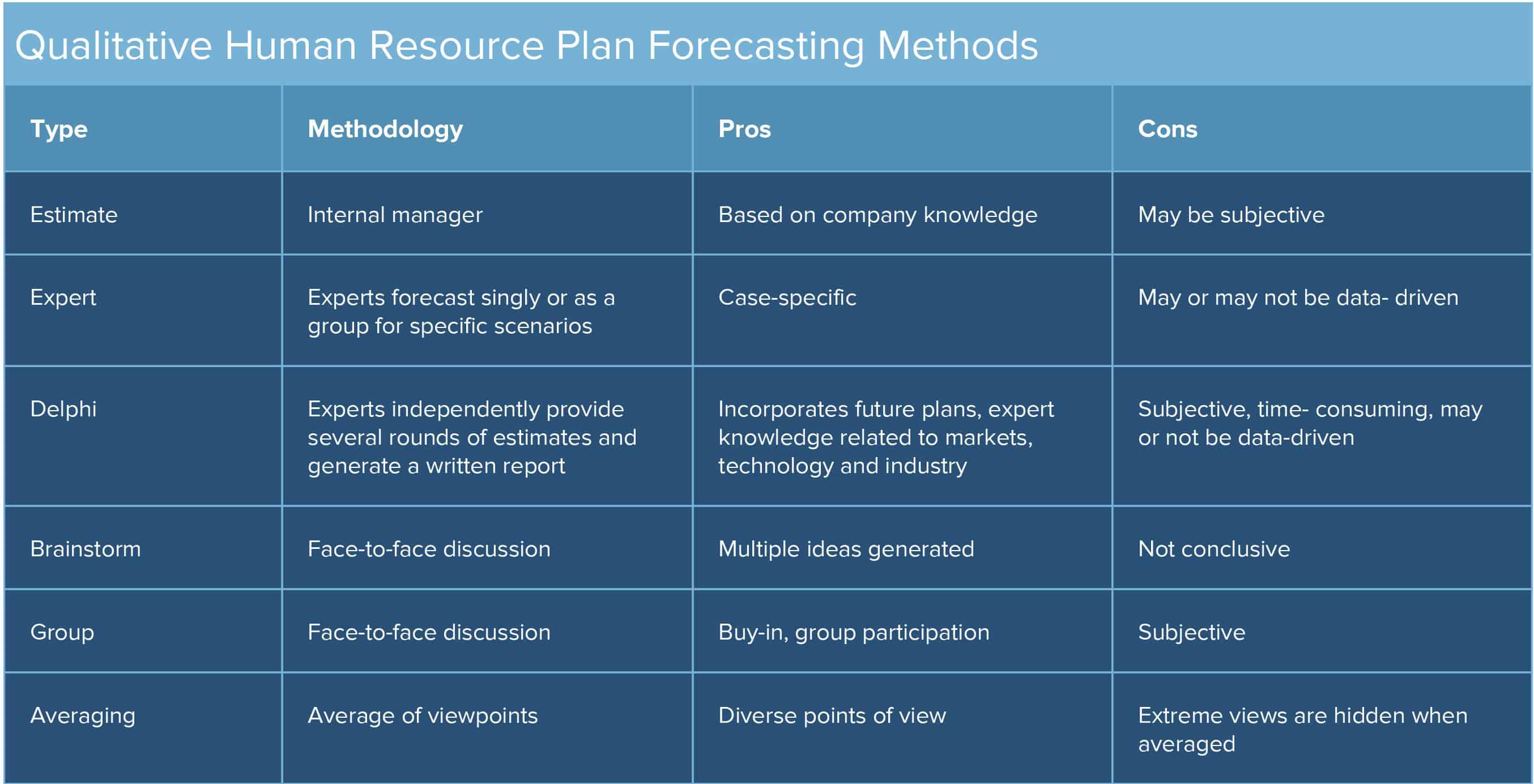
There are two categories of forecasting methods: quantitative and qualitative. You can use both methods to track the work performance of the workforce as a whole, individuals, or business units. Qualitative reports contain anecdotal observations, while quantitative data is statistical or more data-driven. Select the methods that make the most sense in your environment. For example, in a non-manufacturing company, the work-study method which calculates the necessary working hours to produce units may not make sense. By gathering both quantitative and qualitative information, you can identify issues that are impacting your business's productivity, and then develop a well-rounded forecast to increase the company's efficiency, ensure you’re not over or understaffed, and understand future needs.
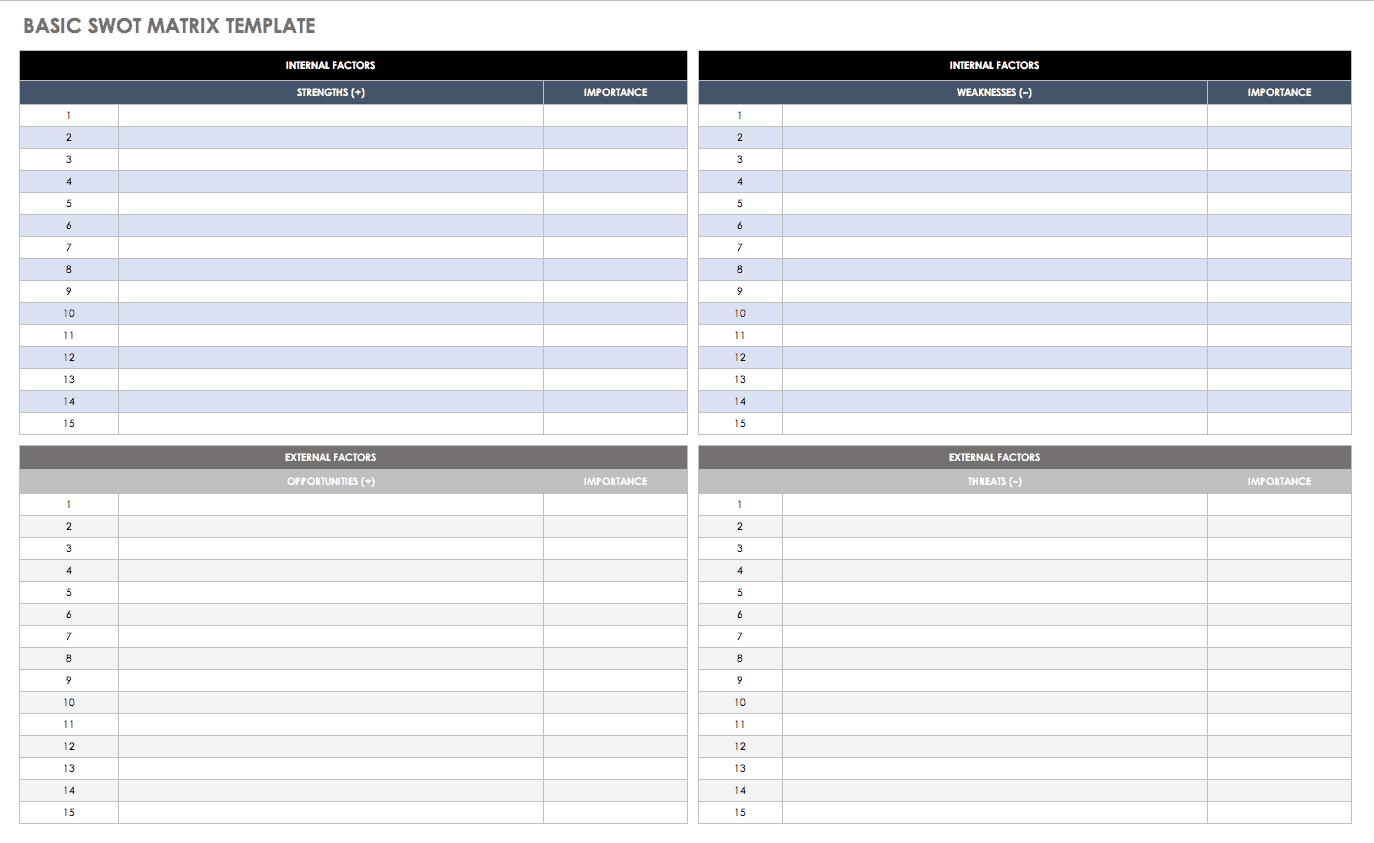
SWOT Matrix Template
The classic SWOT layout provides a clear view of your compiled findings as they relate to your human resources plan. The template also includes a column for rating the importance of each item by category so you can have a clear understanding of how the analysis elements compare and which will need the most attention. You can add Excel worksheets to hold supporting data and clarify the basis of your findings.
Download Basic SWOT Matrix Template
If you’re looking for different formats in Excel, PowerPoint, or Word, you can find free SWOT templates here.
Step Four: Estimate Gaps
With your forecast completed, you’ll have an understanding of future needs and if you will need to fill them with external workers hired full-time, part-time, or as contractors. If you have the right number of employees that don’t have the right skills, you can use training and development to upgrade employee skills to fill the gaps, or you may need to deploy workers in another role.
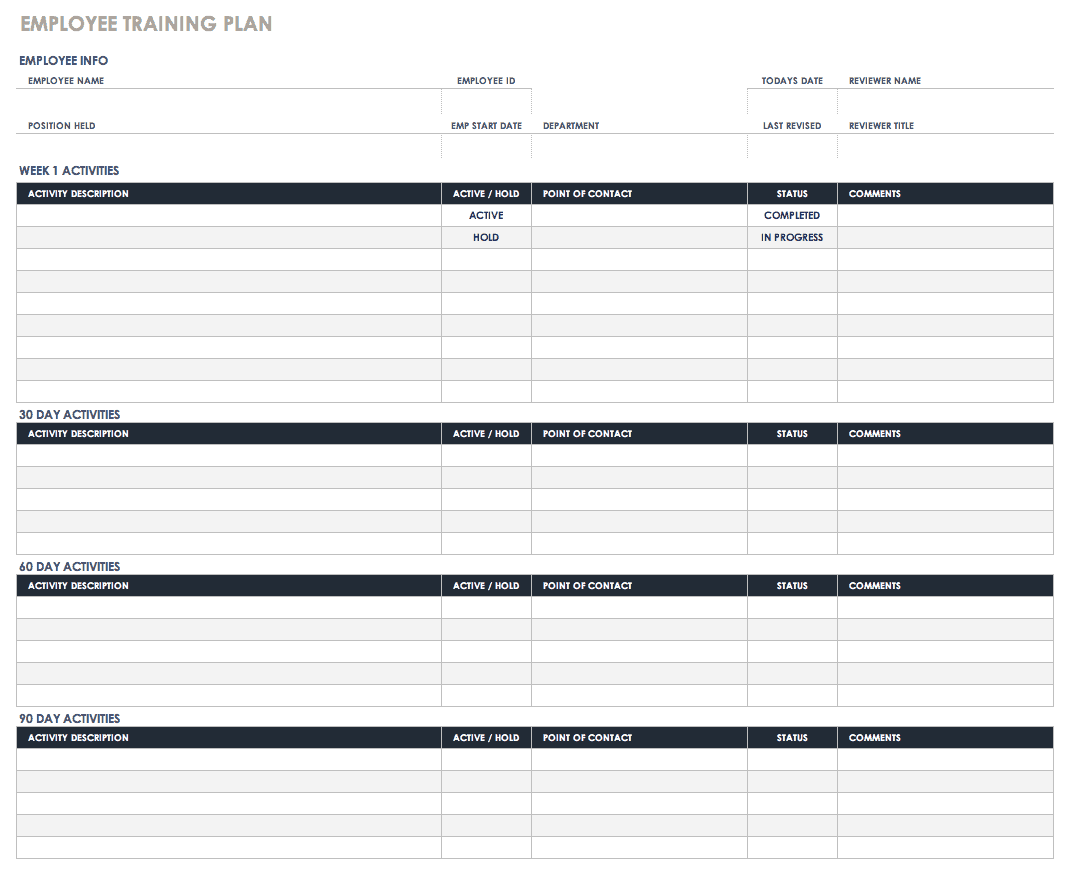
Employee Training Plan Template
Training is relevant for both employee success and team member retention. Though training takes time and effort, it's essential to have a plan in place to ensure a productive ramp-up period for new employees or existing employees who are learning the tasks and responsibilities of a new role. With this adaptable employee training schedule template, you can create training activities lists, add details about which team members need help to complete each task, track status, and provide a way for the manager and employee to enter feedback.
Download Employee Training Template
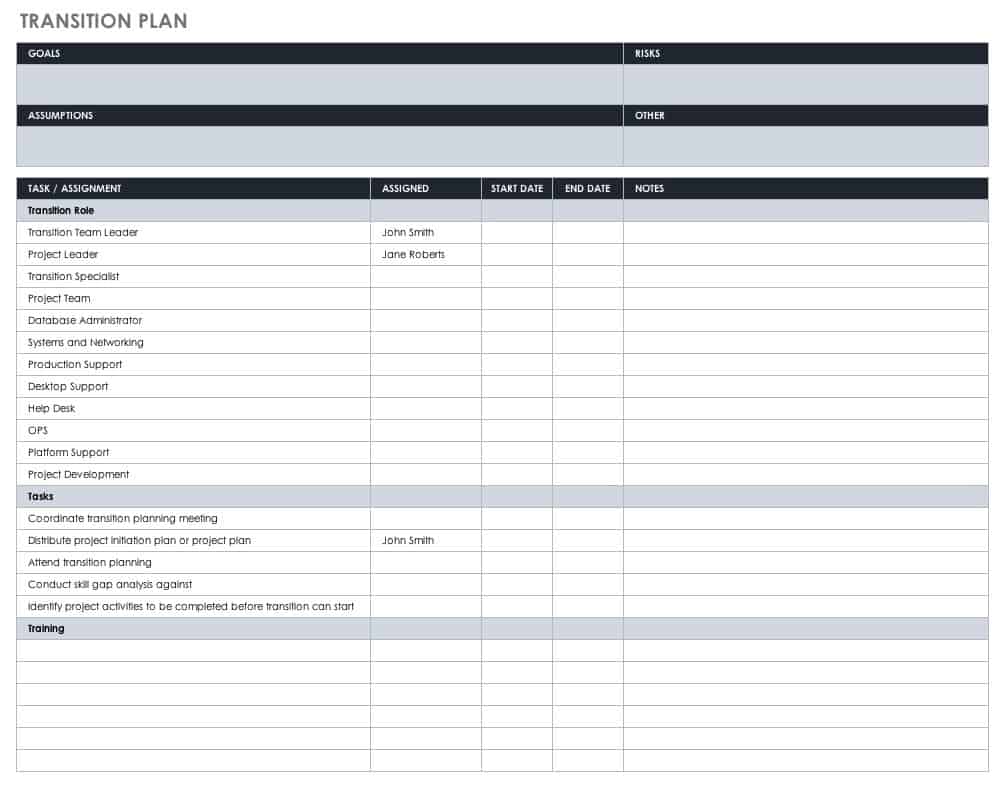
Transition Plan Template
Moving team members to fill different roles can be the ideal solution to filling workforce gaps. When making these changes, ensure that you maintain the information and knowledge the employee had in the initial role. An employee transition plan keeps the information accessible and easy to share. You can also use this transition plan template to assist the person previously in the role train any new team members. Input every aspect of the role that will be useful in the present and future.
Download Transition Plan Excel Template
Step Five: Formulate the Human Resource Action Plan
The human resource plan relies on identifying deficits or surplus in the company. You’ll need to determine if you need to begin recruiting or training, transition, or develop voluntary retirement processes and redeployment in case of a surplus. Include priorities and critical planning issues in your plan.
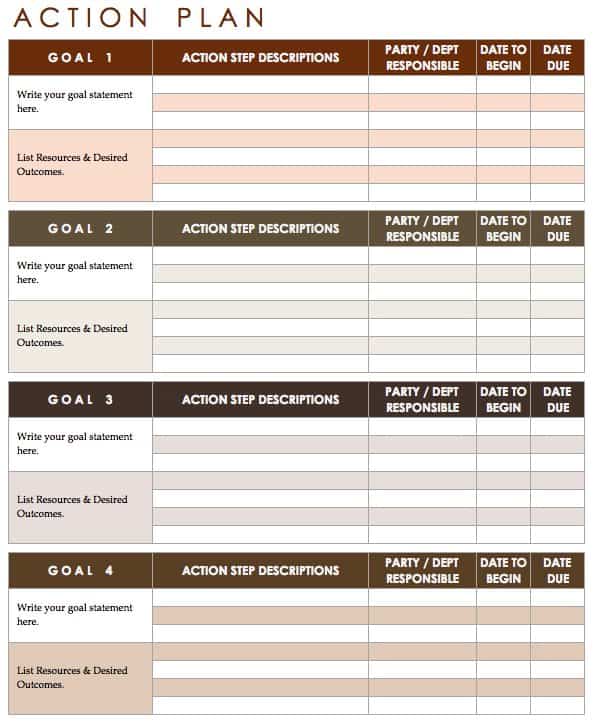
Action Plan Template
This action plan template provides sections for goals, but you can add more sections to customize it to complete your human resources plan. Goals are translated into actionable steps that you can track to check progress. Assign start and end dates for each action, and take notes about each part of the plan.
Download Action Plan Template
Step Six: Integrating/Implementing the Plan
This is the most challenging aspect of any human resources plan. The organization often invests time and money on plans that are shelved and not utilized. Company executives need to grant buy-in, embrace the plan, and bring the organization on board. Overcome any potential employee resistance to the process by rolling in one aspect of the plan at a time to help employees acclimate to changes.
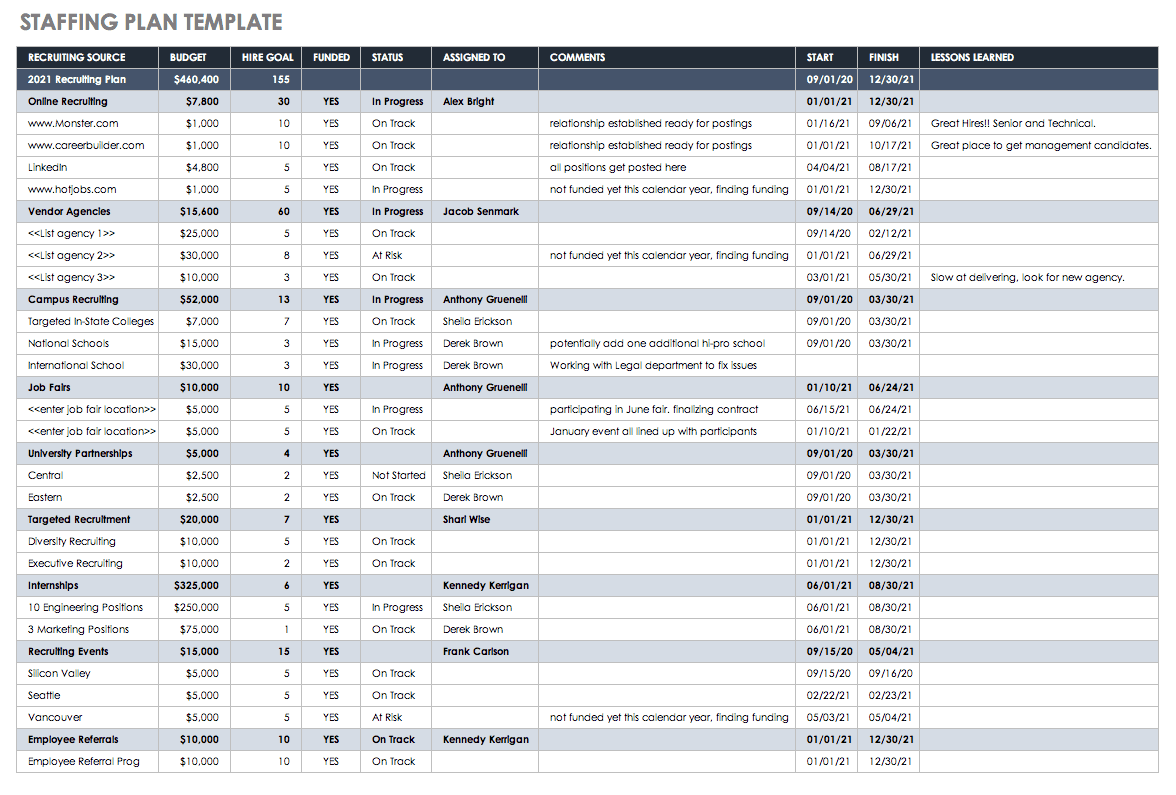
Staffing or Recruiting Plan
Recruitment is one of the top responsibilities of any human resources team. Searching for, vetting, and finding the right talent to join your team are all crucial steps to ensure the success of your organization. Having a staffing plan in place makes your team aware of the available recruitment sources, hiring goals, and budget. Use this staffing plan to organize all staffing details with columns for budgets, hiring goals, status, and comments.
Download Staffing Plan Excel Template
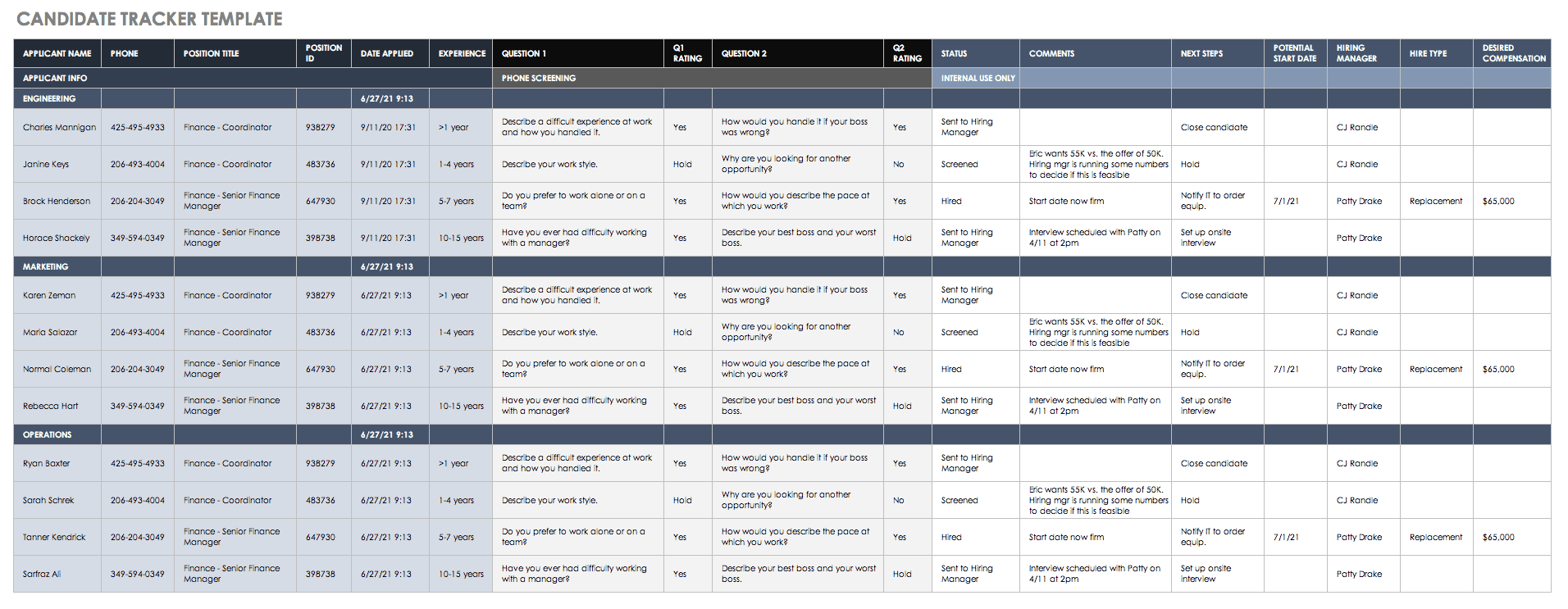
Candidate Screening Tracker
If you don’t have an automated system, you can track and manage applicants’ cover letters, resumes, applications, and details about job openings. Tracking this information can be a lot of work depending on the size of the company and current hiring plan. Use this candidate tracker template to organize candidate documentation and details, and ensure that you provide a positive experience for candidates and people involved in the interview process. Track candidate contact information, phone interview questions and answers, status, comments, next steps, and more using this template.
Download Candidate Tracker Excel Template
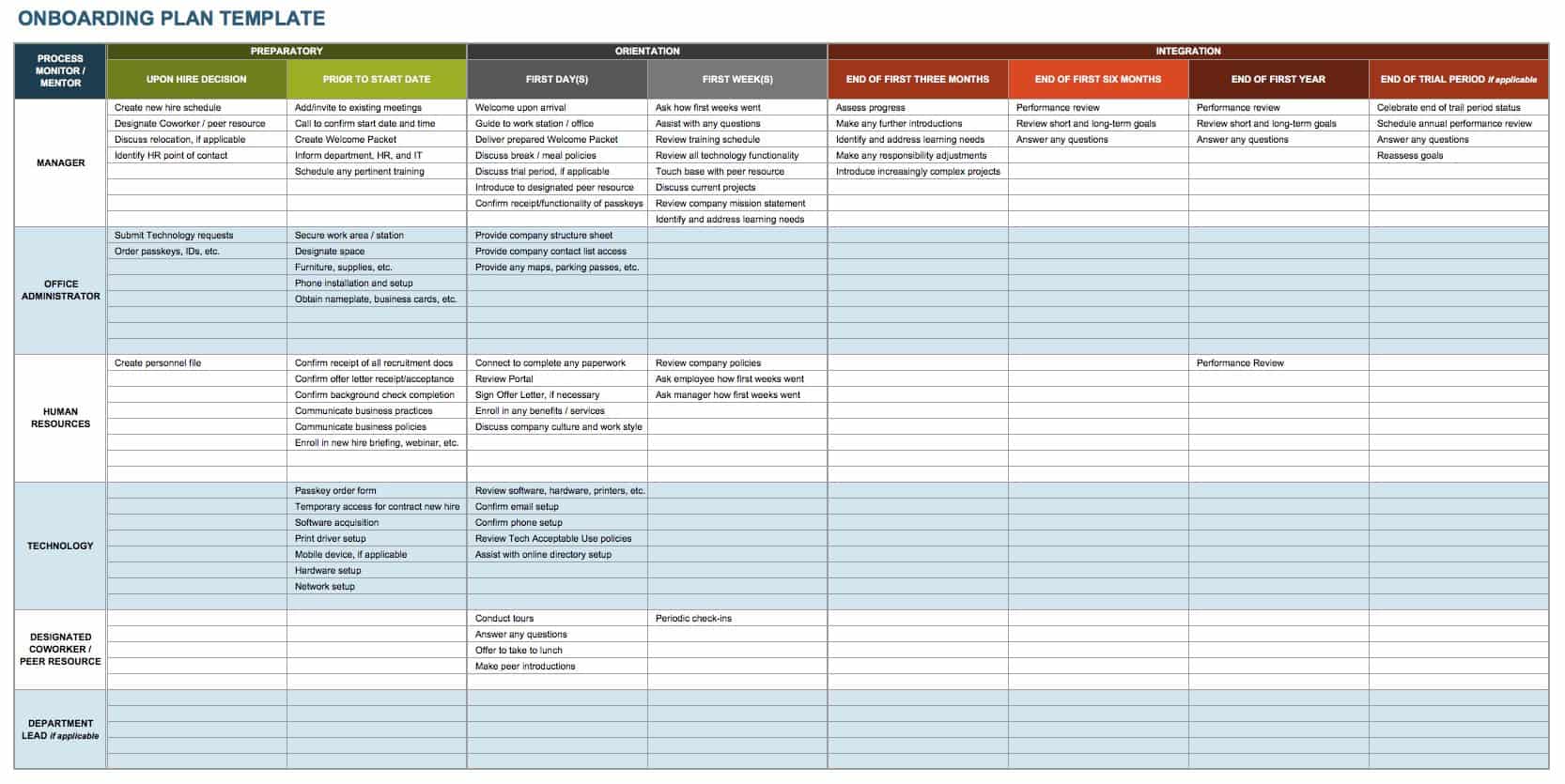
Onboarding Plan Template
Onboarding ensures proper training and enculturation for new team members, and is also a powerful retention tool for any organization. Develop your own onboarding plan by using this template to plan activities at each stage of the process. Since a full year of onboarding is a best human resources practice, this spreadsheet shows tasks assigned to individual contacts over a twelve-month period. Add or remove columns to create a comprehensive onboarding plan.
Download Onboarding Plan Template
For more best practice information and free templates to support your human resources planning, read Top Excel Templates for Human Resources.
Step Seven: Monitoring, Control, and Feedback
Strictly monitoring progress helps identify sticking points in your plan and helps you avoid making changes too quickly. It’s essential to compare actions to how the plan is being implemented to ensure fidelity. The human resource plan is an evergreen document that takes changing circumstances into account. Ongoing measurement, reporting, and continuous improvement efforts will keep the company moving towards its stated strategic goals.
Project Management Dashboard Template
Monitoring all the changes you need to while executing a complicated human resources plan can be time consuming. With this customizable project management dashboard, you can compile every aspect of the process, share status information with management and other team members, and view the big picture at a glance.
Download Excel Project Management Dashboard
Forecasting Is an Ongoing Process
“HRP plans should be reviewed annually, just after the business completes its strategic planning and forecasting for the year,” says Handrick. “For example, if the business plans to open an additional manufacturing location, or offer additional services requiring tech skills not currently in place, then HR will come along and provide estimates as to how many FTEs, what roles, and what kind of skills will be needed. HRP helps with the budgeting for the next fiscal year, and once approved can get to work filling those roles. In a fast-moving environment, HRP may need to be updated with every major change. For example, let's say your organization is project based and you just won a huge contract. Right away your HRP team will need to work with project managers to estimate staffing needs, whether temp or permanent, contract or hire.”
Human Resource Planning Round-Up: Best Practices and Expert Insights
Our experts share their thoughts on some additional issues to keep in mind as you develop your own plan:
- The Importance of Policy Planning: Company policy supports your human resources plan. Policies such as employment classification, benefits, compensation, performance, and improvement are designed to target not only the selection, training, and support of team members, but also to provide guidelines for conduct in and out of the work environment and many other aspects of employment.
- Social Media as Friend and Foe: Social media sites like LinkedIn and Twitter can be powerful recruiting platforms and a friendly, fun way to communicate with team members. However, they can also potentially be an issue when disgruntled employees or competitors get into negative commentary. It’s important to be alert to your company’s social media profile and to take corrective action when the buzz may not be favorable to your goals.
- Strategic Thinking and Human Resources: Burr points out the need for human resources to think creatively and strategically. He says, “Every company should have their own forecasting model and often times, each functional area of the business would need to have a different model as well. While a customer service department may be able to use a data-driven formula for when they need to add people to support call volumes, it is not always as easy to forecast people’s needs in more administrative or managerial capacities.
It’s important to build a set of assumptions about the drivers of work and how growth or contraction in the business would impact the number of people needed and how those should be deployed.” - The “New” Human Resources Professional: “Ultimately, a good HR person is a good business person,” says Adler. “The best HR professionals are system and integration project managers who understand deadlines and highly complex projects. A great candidate has business experience in something other than HR. In my consulting work, I’ve told CEOs that they should look for HR managers with a business background. I think it’s an important consideration, particularly for large firms.”
- More About Markov Predictive Analysis Modeling: One of the most difficult analyses to execute and potentially one of the most valuable tools in forecasting is the Markov model. It’s not a quick fix, but for most mid-to-large companies, it’s worth the time investment to learn how to execute it. For a detailed explanation, read A Markov Model for Human Resources Supply Forecast Dividing the HR System into Subgroups.
- Leadership and Succession Planning: “HR plays a critical role in enabling leadership, in mature or scaling organizations, to anticipate and understand the talent capabilities that will be necessary to meet their strategic objectives,” says Margules. She lists four items:
- HR should have a seat at the table when the strategy is being conceived to align on what capabilities are needed, and by when, to realize the strategy.
- HR needs to influence progressive and aggressive budgeting for resource acquisition, training, coaching, and development every year.
- HR must institutionalize effective succession and talent planning practices at all levels, and build an adaptive organization that can flex its structure to optimize performance.
- HR must use far-reaching ideas to retain its key talent and sustain a highly-engaged workforce in a diverse and driven culture.
- Plan Implementation: “HR plans should align with business strategy and annual plans and should be adaptive to a volatile and uncertain business climate,” says Margules. “While many organizations take a reactive, in-service approach to HR planning and determine their priorities and plans largely in support of annual plans, the most effective organizations are proactive: They anticipate needs and build plans that achieve short term and long term objectives. They adopt progressive practices such as allocating a portion of the staffing budget and resources to recruit and hire key talent for future-focused work. And, they have enough foresight to invest in high potential programs at multiple levels, entry-level accelerated development programs and coaching to build pools of qualified talent for future growth plans.”
- Buy HR Planning Tools or Do It Yourself? “The problem with traditional human resource planning is that it often hasn't supported the scalability of a growing business,” says Burr. “This is precisely why we have to consider new models for talent management, organizational design, and learning and development to ensure that our human resource planning processes can be flexible to meet the scaling needs of the business. This is part of the reason why you have seen an explosion of people analytics tools in the HR marketplace. It is to fill the demand for flexible and scalable models that provide the needed tools for business leaders to plan their people needs as the business grows.”
Adler concurs and says: “I think a spreadsheet can often do a better job. Workforce planning has been around a long time. I think the main point is to be proactive and less reactive in the planning process.”
Five Challenges to Human Resources Planning and Implementation
“People are naturally change- and-risk-averse. Planning and proper support by HR and the people they hire need to happen 100 percent of the time,” says Adler. More often than not, there are some challenges involved in human resources planning and implementation. Here are the five main hurdles:
- Forecasting Is an Imperfect Art: Human resource planning relies on forecasting and supply, which can never be a 100 percent accurate process.
- Resistant Workforce: Employees may feel that their workload will increase, so they resist the process, or they may be uncomfortable altering familiar patterns in their work life and tasks.
- Ambiguity and Rapid Change: Uncertainties such as labor absenteeism, employee turnover, seasonal employment, technological changes and market fluctuations all affect planning.
- Inefficient Information Systems: Human resource information systems need to be reliable, comprehensive, and up to date. It makes it difficult to plan without good data about current employees.
- Cost and Time Factors: With all of the work hours involved in completing and repeating the seven steps, human resource planning is a time consuming and expensive process, so companies sometimes avoid it altogether, despite the benefits.
A Look to the Future of Human Resources Planning
Here are some of the themes experts think will influence human resources professionals, their companies, and the people they hire in the near future:
- Going Global: Globalization, the export of U.S. jobs and the import of non-U.S. employees are already underway, as is offshoring (basing services or processes in different countries). “Globally planning can be complex for any HR professional,” says Burr. “It can be a stressful situation for offshoring and outsourcing of jobs within a firm. HR planning should involve a detailed assessment of the new location globally, the workforce demographics, industry competitors, laws and regulations and the potential impact on U.S. jobs. How do we communicate? How do we train? This will all vary by organization, but a strategic HR plan that communicates the information can lessen the impact. With a sound and detailed HR plan, recruiting, retaining and growing talent within the organization will be much easier.”
“Expect more offshore jobs, outsourcing and contract hiring because frankly they’re cheaper, and in many disciplines like finance, IT, marketing, can do the same work for less,” says Handrick. “Other than providing training for supervisors to manage off-site work teams, there's really no difference for HRP except where the line item goes on the plan. For instance, if you know you'll need 12 FTEs next year, and can get four of them offshore, that line item goes to 'expenses' rather than to 'salary' for the remaining eight.” - More Technology: Social media will likely be in higher use to reach potential workers, particularly millennials who use Twitter, LinkedIn, and Facebook in their job hunts. Telecommuting and the use of social collaboration tools and video conferencing apps will keep people working and in touch with company culture. Emerging platforms will further streamline basic human resources functions to make onboarding and professional development more cost-effective and accessible from anywhere in the world for a virtual workforce.
- Big Data: Metrics and in-depth analysis of processes and people will become increasingly important in human resources as they are in other functional areas. Data- driven decision making is the future, as are metrics to show ROI in people and technology.
- Security Issues: All this new technology brings up security concerns for employers and employee. Data breaches are a fact of life, and the threat to personal data security, company security, and supply chain risks will likely continue.
- Health Care Costs: Costs are likely to continue increasing, since they have been rising steadily in the last several decades. New legislation will perhaps slow the costs of health care. In the meantime, strategies to lower employee healthcare costs will likely take the form of initiatives to improve employee health, and taking advantage of health reimbursement accounts (HRAs) that are consumer-driven or health savings accounts (HSAs).
Improve Human Resources Planning with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.