Step by Step: How to Write a Business Continuity Plan
A business continuity plan refers to the steps a company takes to help it continue operations during a crisis. In order to write a business continuity plan, you gather information about key people, tools, and processes, then write the plan as procedures and lists of resources.
To make formatting easy, download a free business continuity plan template. To learn more about the role of a business continuity plan, read our comprehensive guide to business continuity planning.
- Write a Mission Statement for the Plan: Describe the objectives of the plan. When does it need to be completed? What is the budget for disaster and recovery preparation, including research, training, consultants, and tools? Be sure to detail any assumptions about financial or other resources, such as government business continuity grants.
- Set Up Governance: Describe the business continuity team. Include names or titles and role designations, as well as contact information. Clearly define roles, lines of authority and succession, and accountability. Add an organization or a functional diagram. Select one of these free organizational chart templates to get started.
- Write the Plan Procedures and Appendices: This is the core of your plan. There's no one correct way to create a business continuity document, but the critical content it should include are procedures, agreements, and resources.Think of your plan as lists of tasks or processes that people must perform to keep your operation running. Be specific in your directions, and use diagrams and illustrations. Remember that checklists and work instructions are simple and powerful tools to convey key information in a crisis. Learn more about procedures and work instructions. You should also note who on the team is responsible for knowing plan details.
- Detail a Training Program: Determine the curriculum and timelines for initial and refresher training. "Specify which roles will actively lead training and who must receive training," says Michele Barry, principal consultant at Frontis.
- Set Procedures for Testing Recovery and Response: Create test guidelines and schedules for testing. To review the plan, consider reaching out to people who did not write the plan. Put together the forms and checklists that attendees will use during tests.
- Establish a Process for Capturing Insights: Build debriefs into your processes; these meetings should occur after training sessions and as after-action reports for incidents. "A lesson learned without action is just a lesson observed," explains Alex Fullick, Managing Director at business continuity consultancy Stone Road Inc. "A lot of organizations say, 'We had a situation like this a while ago. What did we do?' If companies take steps on just the lessons learned, they can prepare themselves for many more things."
A business continuity plan is governed by a business continuity policy. You can learn more about creating a business continuity policy and find examples by reading our guide on developing an effective business continuity policy.
How to Create a Business Continuity Plan
Creating a business continuity plan (BCP) involves gathering a team, studying risks and key tasks, and choosing recovery activities. Then write the plan as a set of lists and guidelines, which may address risks such as fires, floods, pandemics, or data breaches.
According to Alex Fullick, your best bet is to create a simple plan. “I usually break everything down into three key categories: people, places, and things. If you focus on a couple of key pieces, you will be a lot more effective. That big binder of procedures is absolutely worthless. You need a bunch of guidelines to say what you do in a given situation: where are our triggers for deciding we’re in a crisis and we have to stop doing XYZ, and just focus on ABC.”
“Post-pandemic, I think new managers will develop more policies and guidelines of all types than required, as a fear response,” cautions Michele Barry.
Because every company is different, no two approaches to business continuity planning are the same. Tony Bombacino, Co-Founder and President of Real Food Blends, describes his company’s formal and informal business continuity approaches. “The first step in any crisis is for our nerve center to connect quickly, assess the situation, and then go into action,” he explains.
“Our sales manager and our marketing manager might discuss what’s going on, and say, ‘Are we going to say anything on social media? Do we need to reach out to any of our customers? The key things, like maintaining stock levels or what if somebody gets sick? What if there's a recall?’ Those plans we have laid out. But we're not a 5,000-person multi-billion-dollar company, so our business continuity plan is often in emails and Google Docs.”
“I've done planning literally for hundreds of businesses where we've just filled out basic forms,” says Mike Semel, President and Chief Compliance Officer of Semel Consulting. “For example, noting the insurance company's phone number — you know, on the back of your utility bill, which you never look at, there's an emergency number for if the power goes out or if the gas shuts off. We've helped people gather all that information and put it down. Even if there's no other plan, just having that information at their fingertips when they need it may be enough.”
You can also approach your business continuity planning as including three types of responses:
- Proactive Strategies: Proactive approaches prevent crises. For example, you may buy an emergency generator to keep power running in your factory, or install a security system to prevent or limit loss during break-ins. Or you may create a bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policy and offer training for remote workers to protect your network and data security.
- Reactive Strategies: Reactive strategies are your immediate responses to a crisis. Examples of reactive methods include evacuation procedures, fire procedures, and emergency response strategies.
- Recovery Strategies: Recovery strategies describe how you resume operations to produce a minimum acceptable level of service. The recovery plan includes actions to stand up temporary processes. The plan also describes the longer-term efforts, such as relocation, data restoration, temporary workaround processes, or outsourcing tasks. Recovery strategies are not limited to IT and data recovery.
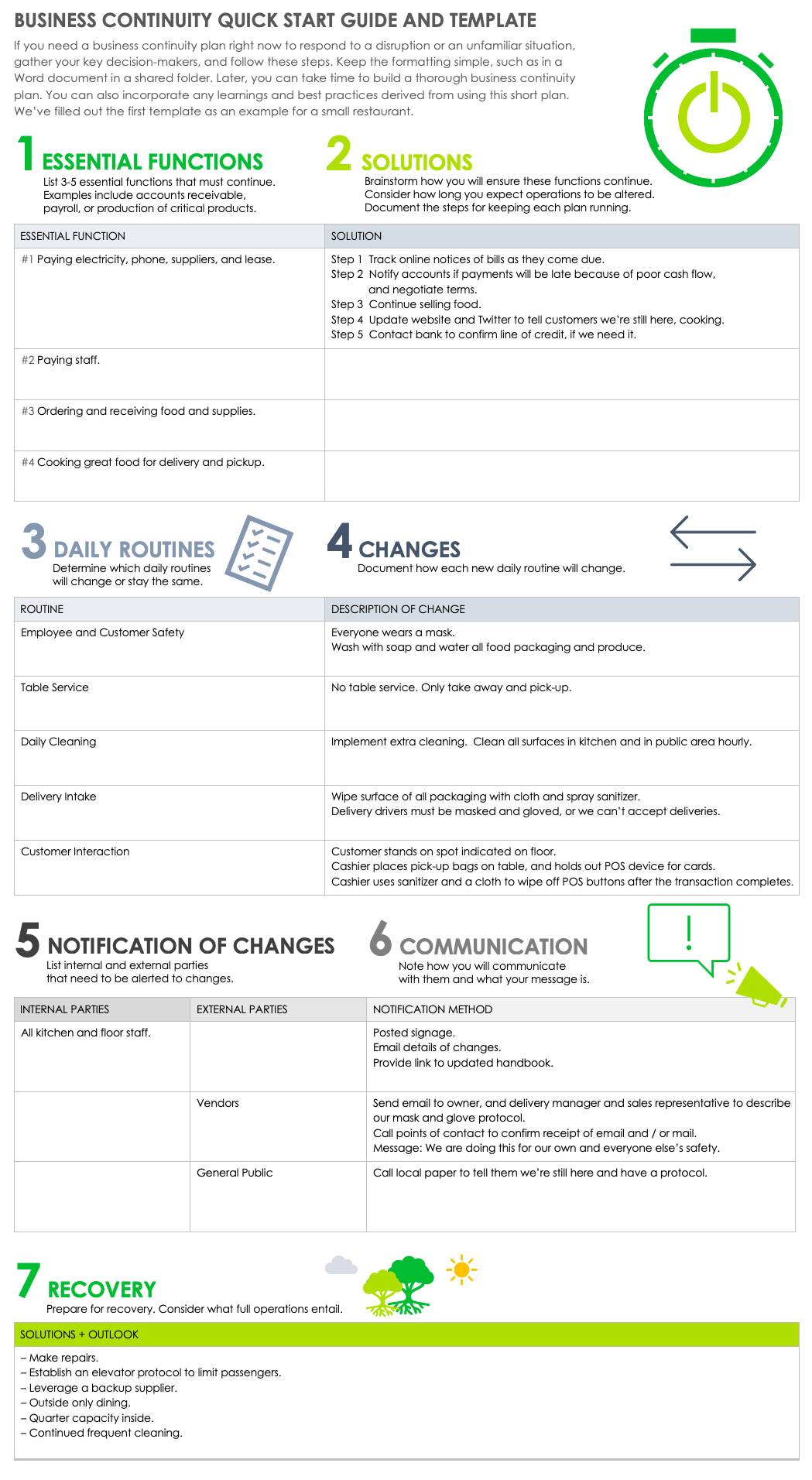
Quick-Start Guide Business Continuity Plan Template
If you don’t already have a business continuity plan in place, but need to create one in short order to respond to a disruption, use this quick-start business continuity template. This template is available in Word and Google Docs formats, and it’s simply formatted so that you can focus on brainstorming and problem-solving.
Download Quick-Start Guide Business Continuity Plan Template
Word | PDF | Google Docs | Smartsheet
For other most useful free, downloadable business continuity plan (BCP) templates please read our "Free Business Continuity Plan Templates" article.
Key Components of a Business Continuity Plan
Your company’s complete business continuity plan will have many details. Your plan may differ from other companies' plans based on industry and other factors. Each facility or business unit may also conduct an impact analysis and create disaster recovery and continuity plans. Consider adding these key components to your business plan:
- Contact Information: These pages include contact information for key employees, vendors, and critical third parties. Locate this information at the beginning of the plan.
- Business Impact Analysis: When you conduct business impact analysis (BIA), you evaluate the financial and other changes in a disruptive event (you can use one of these business impact templates to get started). Evaluate impact in terms of brand damage, product failure or malfunction, lost revenue, or legal and regulatory repercussions.
- Risk Assessment: In this section, assess the potential risks to all aspects of the organization’s operations. Look at potential risks related to such matters as cash on hand, stock levels, and staff qualifications. Although you may face an infinite number of potential internal and external risks, focus on people, places, and things to keep from becoming overwhelmed. Then analyze the effects of any items that are completely lost or need repairs. Also, understand that risk assessment is an ongoing effort that works in tandem with training and testing. Consider adding a completed risk matrix to your plan. You can create one using a downloadable risk matrix template.
- Critical Functions Analysis and List: As a faster alternative to a BIA, a critical functions analysis reveals what processes are critical to keeping your company running. Examples of critical functions include payroll and wages, accounts receivable, customer service, or production. According to Michele Barry, with a values-based approach to critical functions, you should consider who you really are as a company. Then decide what you must continue doing and what you can stop doing.
- Trigger and Disaster Declaration Criteria: Here, you should detail how your executive management will know when to declare an emergency and initiate the plan.
- Succession Plan: Identify alternate staff for key roles in each unit. Schedule time throughout the year to observe alternates as they make important decisions and complete recovery tasks.
- Alternate Suppliers: If your goods are regulated (i.e., food, toy, and pharmaceutical manufacturing), your raw resources and parts must always be up to standard. Source suppliers before a crisis to ensure that regulatory vetting and approval do not delay supplies.
- Operations Plan: Describe how your organization will resume and continue daily operations after a disruption. Include a checklist with such items as supplies, equipment, and information on where data is backed up and where you keep the plan. Note who should have copies of the plan.
- Crisis Communication Strategy: Detail how the organization will communicate with employees, customers, and third-party entities in the event of a disruption. If regular communications systems are disabled, make a plan for alternate methods. Download a free crisis communication strategy template to get started on this aspect.
- Incident Response Plan: Describe how your organization plans to respond to a range of likely incidents or disruptions, and define the triggers for activating the plan.
- Alternate Site Relocation: The alternate site is the location that the organization moves to after a disruption occurs. In the plan, you can also note the transportation and resources required to move the business and the processes you must maintain in this facility.
- Interim Procedures: These are the critical processes that must continue, either in their original or alternate forms.
- Restoration of Critical Data: Critical data includes anything you must immediately recover to maintain normal business functions.
- Vendor Partner Agreements: List your organization’s key vendors and how they can help you maintain or resume operations.
- Work Backlog: This includes the work that piles up when systems are shut down. You must complete this work first when processes start again.
- Recovery Strategy for IT Services: This section details the steps you take to restore the IT processes that are necessary to maintain the business.
- Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO): RTO refers to the maximum amount of time that a company can stop its processes and the length of time without access to data before productivity substantially drops. Determine RTOs for each unit, factoring in people, places, and things.
- Backup Plans: What if plans, processes, or resources fail or are unavailable? Determine alternatives now, so you don't have to scramble. Decide on a backup roster for personnel who are unavailable.
- Manual Workarounds: This section details how a business can operate by hand, should all failsafe measures break down.
- External Audit Details: For regulated organizations, external audits may be compulsory. Your scheduled internal audits will prepare you for external audits.
- Test and Exercise Plan: Identify how and when you will test the continuity plan, including details about periodic tabletop testing and more complex real-world scenario testing.
- Change Management: Note how you will incorporate learnings from tests and exercises, disseminate changes, and review the plan and track changes.
Key Resources for Business Continuity
To fix problems, restore operations, or submit an insurance claim, you need readily available details of the human resources and other groups that can assist with business continuity. (Your organization's unique situation may also require specific types of resources.) Add this information to appendices at the back of your continuity plan.
Fullick suggests broadening the definition of human assets. "People are our employees, certainly. But we forget that the term ‘people’ includes executive management. Management doesn't escape pandemics or the flu or a car crash. Bad things can happen to them and around them, too."
Use the following list as a prompt for recording important information about your organization. Your unique situation may require other types of information.
People:
- Lists of key employees and their contact information. Also, think beyond C-level and response team members to staff with long-term or specialized knowledge
- Disaster recovery and continuity team contact names, roles, and contact information
- Emergency contact number for police and emergency services for your location
- Non-emergency contact information for police and medical
- Emergency and non-emergency contact numbers for facilities issues
- Board member contact information
- Personnel roster, including family or emergency contact names and numbers for the entire organization
- Contractors for any repairs
- Client contact information and SLAs
- Insurance contacts for all plans
- Key regulatory contacts.
- Legal contacts
- Vendor contact information and partner agreements and SLAs
Places:
- Addresses and details for each office or facility
- Primary and secondary contact and information for each facility or office, including at least one phone number and email address
- Off-site recovery location
- Addresses and access information for storage facilities or vehicle compounds
Things:
- Funding and banking information
- IT details and data recovery information, including an inventory of apps and license numbers
- Insurance policy numbers and agent contact information for each plan, healthcare, property, vehicle, etc.
- Inventory of tangibles, including equipment, hardware, supplies, fixtures, and fittings (if you are a supplier or manufacturer, include an inventory of raw materials and finished goods)
- Lease details
- Licenses, permits, other legal documents
- List of special items that you use regularly, but don't order frequently
- Location of backup equipment
- Utility account numbers and contact information (for electric, gas, telephone, water, waste pickup, etc.)
Activities to Complete Before Writing the Business Continuity Plan
Before you write your plan, take these preliminary steps to assemble a team and gather background information.
- Form a team to write the plan. Determine the command and control teams, or who's in charge in a crisis. First and foremost, your organization requires a business continuity coordinator who's sufficiently knowledgeable about processes to delegate tasks. "Bring people into the planning," says Barry. "I think team engagement is something that people often overlook. When you reflect on why things didn't work, you go, 'We just didn't have the right people at the table. We missed out on using skills that we already had.'"
When planning, include the people that must be involved in each process. Divide departments into teams that will help maintain the crucial business functions. Additionally, each department should have both a team leader and a backup team leader. Also, consider including third-party representatives who can help coordinate the supply chain, emergency services, and other activities.
Consider task-oriented roles and teams, such as the following:- Incident Commander: This person is responsible for all aspects of an emergency response.
- Emergency Response Team: The emergency response team refers to the group of people in charge of responding to an emergency or disruption.
- Information Technology Recovery Team: This group is responsible for recovering important IT services.
- Alternate Site/Location Operation Team: This team is responsible for maintaining business operations at an alternate site.
- Facilities Management Team: The facilities management team is responsible for managing all of the main business facilities and determining the necessary responses to maintain them in light of a disaster or disruption.
- Department Upper Management: This includes key stakeholders and upper management employees who govern BCP decisions.
- Conduct business impact analysis or critical function analysis. Understand how the loss of processes in each department can affect internal and external operations. See our article on business continuity planning to learn more about BIAs.
- Conduct risk analysis. Determine the potential risks and threats to your organization.
- Identify the scope of the plan. Define where the business continuity plan applies, whether to one office, the entire organization, or only certain aspects of the organization. Use the BIA and risk analysis to identify critical functions and key resources that you must maintain. Set goals to determine the level of detail required. Set milestones to track progress in completing the plan. "Setting scope is essential," Barry insists. "You need to define the core and noncore aspects of the business and the minimum requirements for achieving continuity."
- Strategize recovery approaches: Strategize how your business should respond to a disruption, based on your risk assessment and BIA. During this process, you determine the core details of the BCP, add the key components and resources, and determine the timing for what must happen before, during, and after a disruptive event.
Common Structure of a Business Continuity Plan
Knowing the common structure should help shape the plan — and frees you from thinking about form when you should be thinking about content. Here is an example of a BCP format:
- Business Name: Record the business name, which usually appears on the title page.
- Date: The day the BCP is completed and signed off.
- Purpose and Scope: This section describes the reason for and span of the plan.
- Business Impact Analysis: Add the results of the BIA to your plan.
- Risk Assessment: Consider adding the risk assessment matrix to your plan.
- Policy Information: Include the business continuity policy or policy highlights.
- Emergency Management and Response: You can detail emergency response measures separately from other recovery and continuity procedures.
- The Plan: The core of the plan details step-by-step procedures for business recovery and continuity.
- Relevant Appendices: Appendices can include such information as contact lists, org charts, copies of insurance policies, or any supporting documents relevant in a crisis.
Keep in mind that every business is different — no two BCPs look the same. Tailor your business continuity plan to your company, and make sure the document captures all the information you need to keep your business functioning. Having everything you need to know in an emergency is the most crucial part of a BCP.
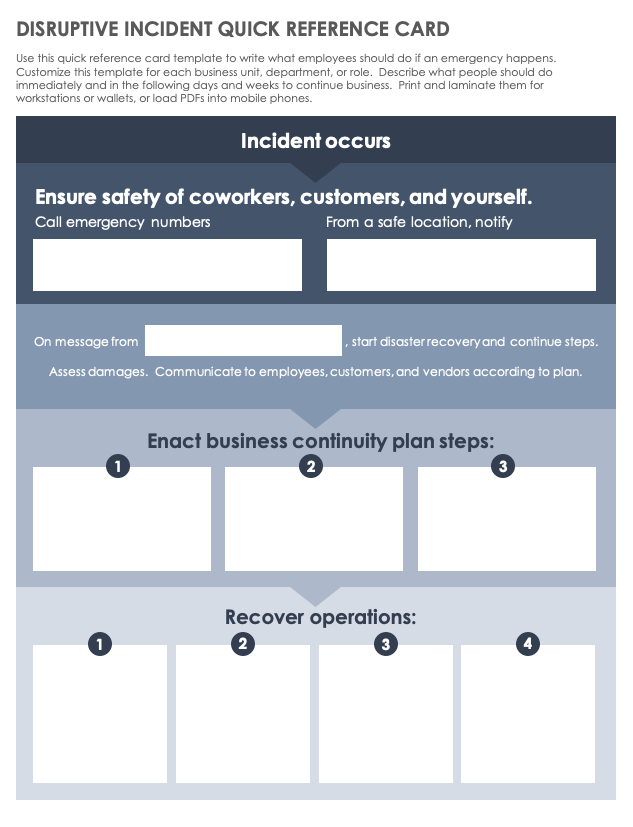
Disruptive Incident Quick-Reference Card Template
Use this quick-reference card template to write the key steps that employees should take in case of an emergency. Customize this template for each business unit, department, or role. Describe what people should do immediately and in the following days and weeks to continue the business. Print PDFs and laminate them for workstations or wallets, or load the PDFs on your mobile phone.
Download Disruptive Incident Quick-Reference Card Template
Expert Disaster Preparation Checklist
Business continuity and disaster planning aren’t just about your buildings and cloud backup — it’s about people and their families. Based on a document by Mike Semel of Semel Consulting, this disaster checklist helps you prepare for the human needs of your staff and their families, including food, shelter, and other comforts.
Tips for Writing a Business Continuity Plan
With its many moving parts and considerations, a business continuity plan can seem intimidating. Follow these tips to help you write, track, and maintain a strong BCP:
- Process
- Take the continuity management planning process seriously.
- Interview key people in the organization who have successfully managed disruptive incidents.
- Get approval from leadership early on and seek their ongoing championship of continuity preparedness.
- Be flexible when it comes to who you involve, what resources you need, and how you achieve the most effective plan.
- Writing
- Keep the plan as simple and targeted as possible to make it easy to understand.
- Limit the plan to practical disaster response actions.
- Base the plan on the most up-to-date, accurate information available.
- Plan for the worst-case scenario and broadly cover many types of potential disruptive situations.
- Consider the minimum amount of information or resources you need to keep your business running in a disaster.
- Use the data you gather in your BIA and risk analysis to make the planning process more straightforward.
- Training and Maintenance
- Share the plan and make sure employees have a chance to review it or ask questions.
- Make the document available in hard copy for easy access, or add it to a shared platform.
- Continually test, review, and maintain your plan to keep it up to date.
- Keep the BCP current with organizational and regulatory changes and updates.
Empower Your Teams to Build Business Continuity with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.